Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image distance (v) with object distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow, without doing any calculations:
| S. No. | Object distance u(cm) | Image distance v(cm) |
| 1 | −90 | +18 |
| 2 | −60 | +20 |
| 3 | −30 | +30 |
| 4 | −20 | +60 |
| 5 | −18 | +90 |
| 6 | −10 | +100 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct. How did you arrive at this conclusion?
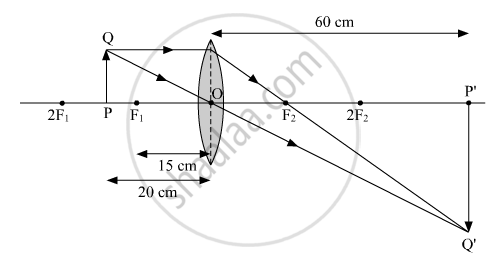
(c) Take an appropriate scale to draw ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
उत्तर
(a) from S.No 3 we can say that the radius of curvature of the lens is 30 cm because when an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a convex lens its image is formed on the other side of the lens at the same distance from the lens. And, we also know that focal length is half of the radius of curvature. Thus, focal length of the lens is + 15 cm.
(b) S.No: 6 is not correct as the object distance is between focus and pole so for such cases the image formed is always virtual but in this case a real image is forming as the image distance is positive.
(c) Approximate value magnification for object distance - 20 cm and image distance + 60 cm is 3.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student obtains a blurred image of a distant object on a screen using a convex lens. To obtain a distinct image on the screen he should move the lens
(A) away from the screen
(B) towards the screen
(C) to a position very far away from the screen
(D) either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the object
Which type of mirror has:
positive focal length?
Which type of mirror has:
negative focal length?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
A diverging mirror is used as a rear-view mirror.
What happens to the image when the object is moved away from the mirror gradually?
The image formed by a spherical mirror is virtual. The mirror will be:
(a) concave
(b) convex
(c) either concave or convex
(d) metallic
An object placed 20 cm in front of a mirror is found to have an image 15 cm (a) in front of it, (b) behind the mirror. Find the focal length of the mirror and the kind of mirror in each case.
At the point of incidence, a line drawn at right angles to the surface, separating the two media, is called the normal.
A .............. mirror is obtained on silvering the outer surface of a part of a hollow glass sphere.
Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles
