Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer in brief.
Explain the relationship between Income and Consumption.
उत्तर
The relation between the consumption and the income is depicted by the consumption function, also known as ‘Propensity to Consume’. It depicts how a change in the income causes a change in the consumption pattern of an individual.
C = f(Y)
Where,
C represents consumption expenditure
Y represents aggregate income; and
f represents the functional relationship between the consumption expenditure and the level of the disposable income.
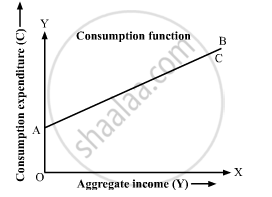
According to this, as the income increases, the consumption expenditure also increases. however, the increase in the consumption expenditure is less than the increase in income.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
............... consumption can not be zero.
(Induced / Autonomous / Government / Private)
Distinguish between marginal propensity to consume and average propensity to consume. Give a numerical example.
Complete the following table:-
| Income (Rs) | Consumption expenditure (Rs) | Marginal propensity to save | Average propensity to save |
| 0 | 80 | ||
| 100 | 140 | 0.4 | ....... |
| 200 | ........ | ...... | 0 |
| ....... | 240 | ........ | 0.20 |
| ......... | 260 | 0.8 | 0.35 |
Find equilibrium national income:
Autonomous consumption expenditure = 120
Marginal propensity to consume = 0.9
Investment expenditure = 1100
In an economy an increase in investment by Rs 100 crore led to ‘increase’ in national by Rs 1000 crore. Find marginal propensity to consume.
An economy is in equilibrium. Find marginal propensity to consume :
Autonomous consumption
Expenditure = 100
Investment expenditure = 100
National Income = 2,000
An economy is in equilibrium. Find autonomous consumption expenditure:
National Income =1,600
Investment Expenditure = 300
Marginal Propensity to Consume= 0.8
An economy is in equilibrium. From the following data about an economy calculate autonomous consumption.
1) Income = 500
2) Marginal propensity to save = 0.2
3) Investment expenditure = 800
Assuming that increase in investment is Rs. 800 crore and marginal propensity to consume is 0.8, explain the working of multiplier
An economy is in equilibrium. From the following data calculate autonomous consumption.[4]
(i) Income = 10,000
(ii) Marginal propensity to consume = 0.2
(iii) Autonomous consumption = 1,500
An economy is in equilibrium. From the following data, calculate the marginal propensity to save:
1) Income = 10,000
2) Autonomous consumption = 500
3) Consumption expenditure = 8,000
An economy is in equilibrium. Find Marginal Propensity to Consume from the following:
National income = 2000
Autonomous consumption = 400
Investment expenditure = 200
An economy is in equilibrium. Calculate the Investment Expenditure from the following
National Income = 800
Marginal propensity to save = 0.3
Autonomous Consumption = 100
Calculate Marginal Propensity to Consume from the following data about an economy
Which is an equilibrium:
National income = 2000
Autonomous Consumption expenditure = 200
Investment expenditure = 100
An economy is in equilibrium. Calculate Marginal Propensity to Save from the following :
National Income = 1,000
Autonomous Consumption = 100
Investment Expenditure = 200
Complete the following table:
|
Consumption expenditure (Rs) |
Savings (Rs) |
Income (Rs) |
Marginal propensity to Consume |
|
100 |
50 |
150 |
|
|
175 |
75 |
……. |
…… |
|
250 |
100 |
……. |
…… |
|
325 |
125 |
……. |
…… |
Answer the following question :
Explain the development and non-development expenditures of government .
Write explanatory answer
State and explain J.M. Keynes's ‘psychological law of consumption’.
Define or explain the following concept.
Autonomous Consumption.
Distinguish between :
Propensity to consume and Propensity to save.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given in the bracket:
The part of income not spent is________.
Choose the correct answer :
The income which is not spent on consumption is known as _________.
Define or explain the following concept
Marginal Cost.
Answer the following question.
State the objective factors determining consumption function.
Answer the following question.
What is meant by a propensity to consume?
The consumption function of an economy is : C = 40 + 0.8 Y (amount in ₹ crores). Determine that level of income where the average propensity to consume will be one.
If in an economy :
Change in initial Investment (∆I) = ₹ 700 crores
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) = 0.2
(a) Investment Multiplier (k)
(b) Change in final income (∆Y)
In a hypothetical economy, Mr. Neeraj has deposited ₹100 in the bank. If it is assumed that there is no other currency circulation in the economy, then the total money supply in the economy will be ____________.
If the income is ₹ 400 crores and consumption is ₹ 250 crores, what will be the APC?
The relation between APC and MPC in Keynes Psychological consumption function is ______.
Which one is correct?
The relation between consumption and savings are ______
Calculate Change in Income (ΔY) for a hypothetical economy. Given that:
- Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) = 0.8, and
- Change in Investment (ΔI) = Rs. 1,000 crores
______ buy goods and services for consumption and also supply factors of production.
MPC = 1 − MPS. It is ______
Marginal Propensity to Save is equal to ______
Calculate Autonomous Consumption expenditure from the following data about an economy which is in equilibrium:
National Income = Rs 1,200
Marginal Propensity to Save = 0.20
Investment expenditure = Rs 100
What is "MPS" or the 'marginal propensity' to save?
What is saving per Income called?
If the value of Average Propensity to Save (APS) is 0.2 and National Income is ₹4,000 crores, then consumption will be ______
When we add up utility derived from consumption of all the units of the commodities, we get:
The marginal physical product of a factor must be ______ when the total physical product is falling.
Identify the correctly matched pair from Column A to that of Column B:
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (1) | MPC | (a) | Ratio of Savings to Consumption |
| (2) | APC | (b) | Ratio of Consumption to Income |
| (3) | APS | (c) | Ratio of Consumption to Savings |
| (4) | MPS | (d) | Ratio of Savings to Investment |
If increase in National Income is equal to increase in consumption, identity the value of Marginal Propensity to Save:
Assertion (A): Saving curve makes a negative intercept on the vertical axis at zero level of income.
Reason (R): Saving function refers to the functional relationship between saving and income.
In an economy 75 percent of the increase in income is spent on consumption. Investment increased by ₹ 1,000 crore.
Calculate the total increase in income on the basis of given information.
An Economy is in equilibrium, calculate the Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) from the following:
- National Income (Y) = ₹ 4,400
- Autonomous Consumption `bar("C")` = ₹ 1,000
- Investment Expenditure (I) = ₹ 70
Assertion (A): At the break-even level of income, the value of Average Propensity to Consume (APC) is zero.
Reason (R): Sum of Average Propensity to Consume (APC) and Average Propensity to Save (APS) is always equal to one.
Complete the following table:
| INCOME (Y) |
SAVING (S) |
APC |
| 0 | (-) 12 | |
| 20 | 6 |
How is APS obtained from the APC?
