Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer in brief.
How is a Zener diode different than an ordinary diode?
उत्तर
A Zener diode is heavily doped, with doping concentrations greater than 1018 cm-3 in both the p- and n-regions, whereas an ordinary diode has doping concentrations of 1017 cm-3 or less. As a result, the peak inverse voltage (PIV) of an ordinary diode is greater than that of a Zener diode, and the breakdown occurs through impact ionisation (avalanche process). Other than that, their I-V characteristics are similar.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option:
A Series resistance is connected in the Zener diode circuit to ______.
An LED emits visible light when it's ______.
Choose the correct option.
Solar cell operates on the principle of ______.
Answer in brief.
On which factors does the wavelength of light emitted by a LED depend?
Answer in brief.
Why should a photodiode be operated in reverse biased mode?
State the principle of solar cells.
Explain how a Zener diode maintains a constant voltage across a load.
Explain the forward and the reverse characteristic of a Zener diode.
Explain the working of a LED.
Explain the principle of operation of a photodiode.
State any two special-purpose diodes.
State any two advantages and disadvantages of a photodiode.
Define the dark current of the photodiode. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a photodiode?
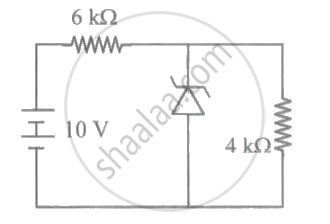
What will be the current flowing through the 6 kΩ resistor in the circuit shown, where the breakdown voltage of the Zener is 6V?
With a neat labelled diagram, explain the working of a photodiode. Calculate the wavelength in angstrom at which the emissive power is maximum for a blackbody heated to 3727 °C.
State the factors which control the wavelength of light emitte d by an LED.
Zener breakdown results from breaking of Si-Si covalent bonds in a silicon junction diode due to ______.
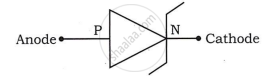
Give the name of the following symbol.
Draw a neat labelled schematic diagram of LED.
Distinguish between light-emitting diode and photo-diode.
What is a Light Emitting Diode?
