Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the forward and the reverse characteristic of a Zener diode.
उत्तर
The forward bias region of a Zener diode is identical to that of a regular diode. There is a forward current only after the barrier potential of the pnjunction is overcome. Beyond this threshold or cut-in voltage, there is an exponential upward swing.
The typical forward voltage at room temperature with a current of around 1 mA is around 0.6 V.
In the reverse bias condition, the Zener diode is an open circuit and only a small reverse saturation current flows as shown with a change of scale. At the reverse breakdown voltage, there is an abrupt rapid increase in the current- the knee is very sharp, followed by an almost vertical increase in current. The voltage across the Zener diode in the breakdown region is very nearly constant with only a small increase in voltage with increasing current. There is a minimum Zener current, Iz (min), that places the operating point in the desired breakdown region. At some high current level, IZM, the power dissipation of the diode becomes excessive beyond which the diode can be damaged.
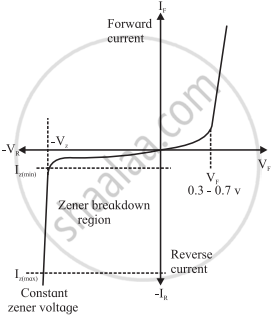
Zener diode characteristics
The I-V characteristics of a Zener diode is not totally vertical in the breakdown region. This means that for slight changes in current, there will be a small change in the voltage across the diode. The voltage change for a given change in current is the resistance Rz of the Zener diode.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option:
A Series resistance is connected in the Zener diode circuit to ______.
An LED emits visible light when it's ______.
Choose the correct option.
Solar cell operates on the principle of ______.
Answer in brief.
How is a Zener diode different than an ordinary diode?
Answer in brief.
On which factors does the wavelength of light emitted by a LED depend?
Answer in brief.
Why should a photodiode be operated in reverse biased mode?
State the principle of solar cells.
Answer in brief.
State the uses of the solar cell.
Explain how a Zener diode maintains a constant voltage across a load.
Explain the working of a LED.
State any two advantages and disadvantages of a photodiode.
Define the dark current of the photodiode. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a photodiode?
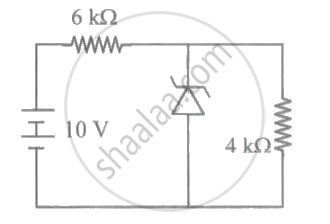
What will be the current flowing through the 6 kΩ resistor in the circuit shown, where the breakdown voltage of the Zener is 6V?
With a neat labelled diagram, explain the working of a photodiode. Calculate the wavelength in angstrom at which the emissive power is maximum for a blackbody heated to 3727 °C.
State the factors which control the wavelength of light emitte d by an LED.
Draw a neat labelled schematic diagram of LED.
Distinguish between light-emitting diode and photo-diode.
What is a Light Emitting Diode?
Draw Light Emitting Diode circuit symbol.
