Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
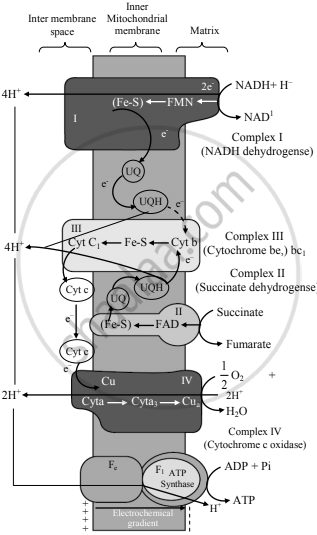
Explain ETS.
उत्तर
- NADH2 and FADH2 produced during glycolysis, connecting link reaction and Krebs cycle are oxidized with the help of various electron carriers and enzymes.
- These carriers and enzymes are arranged on the inner mitochondrial membrane in the form of various complexes as complex I, II, III, VI and V.
- NADH+H+ is oxidized by NADH dehydrogenase (complex I) and it's electrons are transferred to ubiquinone (coenzyme Q-CoQ) present on the inner membrane of mitochondria. Reduced ubiquinone is called as ubiqunol.
- FADH2 is oxidized by complex II (Succinate dehydrogenase) and these electrons are also transferred to CoQ.
- During oxidation of NADH+H+ and FADH2, electrons and protons are released but only electrons are carried forward whereas protons are released into the outer chamber of mitochondria (intermembrane space).
- Ubiquinol is oxidized by complex-III (Cytochrome bc1 complex) and it's electrons are transferred to cytochrome C. Cytochrome C is a small, iron-containing protein, loosely associated with the inner membrane. It acts as a mobile electron carrier, transferring the electrons between complex III and IV.
- Cytochrome C is oxidized by complex IV or cytochrome C oxidase consisting of cytochrome a and a3. Electrons are transferred by this complex to the molecular oxygen. This is terminal oxidation.
- Reduced molecular oxygen reacts with protons to form a water molecule called as metabolic water.
- Protons necessary for this are channelled from the outer chamber of mitochondria into the inner chamber by F0 part of oxysome (complex V) present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This proton channelling by F0 is coupled to the catalytic site of F1 which catalyses the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. This is oxidative phosphorylation. As the transfer of protons is accompanied with a synthesis of ATP, this process is named as 'Chemiosmosis' by Peter Mitchell.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following in detail.
In human beings, what happens to oxygen after it is inhaled through the nose?
Name the following:
A common phase in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Name the following:
The respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
Study the following statements with respect to Krebs cycle and select the correct option.
- As per need, acetyl CoA or some other intermediates like a-ketoglutarate, oxaloacetate of Krebs cycle are used as precursors for synthesis of fatty acids, glutamic acid and aspartic acid respectively.
- Various reactions of Krebs cycle involve step-wise oxidation of acetyl part of acetyl CoA leading to release of energy and C02.
From the following identify the reactions in which ATP is NOT used.
Match the Column I (ETS Complex) to Column II (Characteristic) and select the correct option.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| i. | Complex I | a. | Succinate dehydrogenase |
| ii. | Complex II | b. | Cytochrome oxidase |
| iii. | Complex III | c. | NADH dehydrogenase |
| iv. | Complex IV | d. | Cytochrom bc1 complex |
____________ results into the conversion of oxalosuccinate into α ketoglutarate involves in Krebs cycle.
During glycolysis the compounds PGAL and DHAP are formed from fructose 1, 6 diphosphate by ____________.
Glycolysis occurs in ____________.
