Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Give any four applications of thermal conductivity in everyday life.
उत्तर
- a. Thick walls are used in the construction of cold storage rooms.
b. Brick being a bad conductor of heat is used to reduce the flow of heat from the surroundings to the rooms.
c. Better heat insulation is obtained by using hollow bricks.
d. Air being a poorer conductor than a brick, it further avoids the conduction of heat from outside. - Street vendors keep ice blocks packed in saw dust to prevent them from melting rapidly.
- The handle of a cooking utensil is made of a bad conductor of heat, such as ebonite, to protect our hand from the hot utensil.
- Two bedsheets used together to cover the body help retain body heat better than a single bedsheet of double the thickness. Trapped air being a bad conductor of heat, the layer of air between the two sheets reduces thermal conduction better than a sheet of double the thickness. Similarly, a blanket coupled with a bedsheet is a cheaper alternative to using two blankets.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Explain the term 'steady state'.
Answer the following question.
Derive its expression for the coefficient of thermal conductivity.
Answer the following question.
Explain the term thermal resistance. State its SI unit and dimensions.
Answer the following question.
Which materials can be used as thermal insulators and why?
Solve the following problem.
Which will require more energy, heating a 2.0 kg block of lead by 30 K or heating a 4.0 kg block of copper by 5 K?
(slead = 128 J kg–1 K–1, `"s"_"copper"` = 387 J kg–1 K–1)
Solve the following problem.
The rate of flow of heat through a copper rod with temperature difference 30 °C is 1500 cal/s. Find the thermal resistance of copper rod.
Solve the following problem.
Find the temperature difference between two sides of a steel plate 4 cm thick, when the heat is transmitted through the plate at the rate of 400 k cal per minute per square meter at a steady state. Thermal conductivity of steel is 0.026 kcal/m s K.
Liquid is filled in a vessel which is kept in a room with temperature 20° C. When the temperature of the liquid is 80° C, then it loses heat at the rate of 90 cal/s. What will be the rate of loss of heat when the temperature of the liquid is 40° C?
If 1 g of a steam which is at 100°C starts melting then how much ice will remain at 0° C? (Latent heat of ice = 80 cal/g and latent heat of steam= 540 cal/g)
Heat energy is incident on the surface at the rate of 1000 J/min. If the coefficient of absorption is 0.8 and the coefficient of reflection is 0.1 then heat energy transmitted by the surface in 5 minutes is ______.
A slab consist of two parallel layers of copper and brass of the same thickness and having thermal conductivities in the ratio 1 : 4. If the free face of brass is at 100°C and that of copper at 0°C, the temperature of interface is ______.
A ring consisting of two parts ADB and ACB of same conductivity K carries an amount of heat H. The ADB part is now replaced with another metal keeping the temperatures T1 and T2 constant. The heat carried increases to 2H. What should be the conductivity of the new ADB part? (Given `"ACB"/"ADB"` = 3)
Two rectangular blocks A and B of different metals have same length and same area of cross-section. They are kept in such a way that their cross-sectional area touch each other. The temperature at one end of A is 100°C and that of B at the other end is 0°C. If the ratio of their thermal conductivity is 1 : 3, then under steady state, the temperature of the junction in contact will be ______.
A thin square steel plate with each side equal to 10 cm is heated by a blacksmith. The rate of radiated energy by the heated plate is 1134 watts. The temperature of the hot steel plate is ______.
(Stefan's constant σ = 5.67 × 10-8 watt m-2K-4 emissivity of the plate = 1)
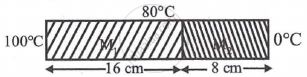
Two metallic blocks M1 and M2 of same area of cross-section are connected to each other (as shown in figure). If the thermal conductivity of M2 is K then the thermal conductivity of M1 will be ______. [Assume steady state heat conduction]
Two rods of the same material, same length and same radius transfer a given amount of heat in t second when they are joined end-to-end. When the rods are joined one above the other, then they will transfer the same heat in the same conditions in time ______.
