Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Write explanatory notes on Glycolysis.
उत्तर
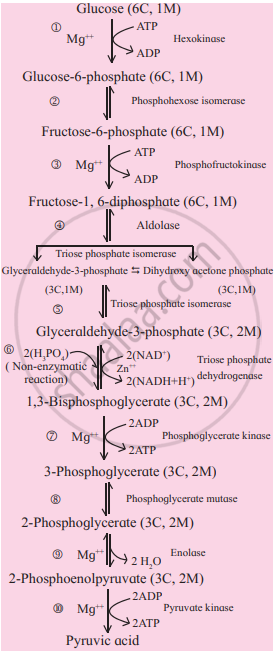
Glycolysis is a process where glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid, hence called glycolysis (glucose-breaking). It is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It involves ten steps.
Glycolysis consists of two major phases:
- Preparatory phase (1-5 steps):
- In this phase, glucose is phosphorylated twice by using two ATP molecules and a molecule of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is formed.
- It is then cleaved into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxy acetone phosphate. These two molecules are 3-carbon carbohydrates (trioses) and are isomers of each other.
- Dihydroxy acetone phosphate is isomerized to the second molecule of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
- Therefore, two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate is formed.
- Preparatory phase of glycolysis ends.
- Payoff phase:
- In this phase, both molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate are converted to two molecules of 1,3- bisphoglycerate by oxidation and phosphorylation. Here, the phosphorylation is brought about by inorganic phosphate instead of ATP.
- Both molecules of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate are converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid through a series of reactions accompanied with the release of energy. This released energy is used to produce ATP (4 molecules) by substrate-level phosphorylation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank.
Muscles of human beings switch to anaerobic ...................... in the absence of oxygen.
Fill in the blank.
In human beings, the exchange of gases takes place in .................... (lungs).
Given below are chemical reactions (1 to 5) involving glucose and five other chemical products (A-E).
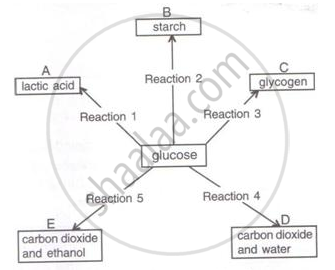
Which reactions (1-5) in the above correspond to the following (write the corresponding number of reaction next to them).
(i) Aerobic respiration
(ii) Change taking place in the liver
(iii) Anaerobic respiration in yeast
(iv) Change taking place in a plant
storage organ, e.g., potato
(v) Anaerobic respiration in animals
Fill in the blank:
The final hydrogen acceptor in aerobic respiration is ______.
Complete the following statement by selecting the correct alternative from the ones given below:
The immediate source of energy for metabolic reactions in a living cell is ______.
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
Where does glycolysis take place?
From the following identify the correct description of anaerobic respiration.
______ NAD molecule get reduced during incomplete oxidation of one glucose molecule.
Complete the following reaction.
C6H1206 + 602 → 6C02 + ______ + 38 ATP
How many ATPs will be effectively produced during the production of 1 molecule of acetyl Co-A from 1 molecule of pyruvic acid?
