Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
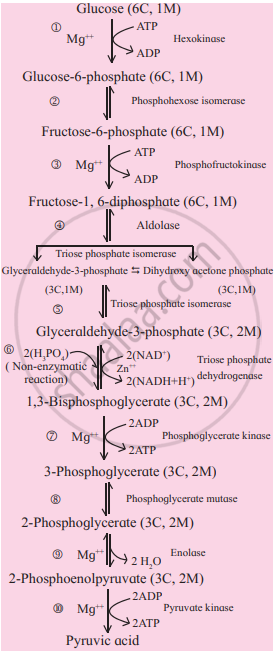
Write explanatory notes on Glycolysis.
Solution
Glycolysis is a process where glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid, hence called glycolysis (glucose-breaking). It is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It involves ten steps.
Glycolysis consists of two major phases:
- Preparatory phase (1-5 steps):
- In this phase, glucose is phosphorylated twice by using two ATP molecules and a molecule of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is formed.
- It is then cleaved into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxy acetone phosphate. These two molecules are 3-carbon carbohydrates (trioses) and are isomers of each other.
- Dihydroxy acetone phosphate is isomerized to the second molecule of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
- Therefore, two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate is formed.
- Preparatory phase of glycolysis ends.
- Payoff phase:
- In this phase, both molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate are converted to two molecules of 1,3- bisphoglycerate by oxidation and phosphorylation. Here, the phosphorylation is brought about by inorganic phosphate instead of ATP.
- Both molecules of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate are converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid through a series of reactions accompanied with the release of energy. This released energy is used to produce ATP (4 molecules) by substrate-level phosphorylation.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following in one word.
What is carbamino hemoglobin?
Mention if the following statement is true or false. If false, rewrite them correctly.
Anaerobic respiration in plants yields lactic acid.
Write True or False against the following statement:
Glycolysis takes place in the crystal of the mitochondria.
Identify the last electron acceptor in ETS.
In which of the conversions, NADH + H+ is not formed?
____________ results into the conversion of oxalosuccinate into α ketoglutarate involves in Krebs cycle.
ATP is used in glycolysis to phosphorylate ______.
β-oxidation of fatty acids produces ____________ as the end product.
Where is the respiratory electron transport system (ETS) located in plants?
____________ catalyzes the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate.
