Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
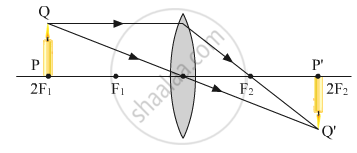
At which position will you keep an object in front of a convex lens so as to get a real image of the same size as the object? Draw a figure.
उत्तर
When an object is placed at the centre of curvature 2F1 of a convex lens, we will get a real image of the same size as the object.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A converging lens has focal length of 12 cm. Calculate at what distance the object should be placed from the lens so that it forms an image at 48 cm on the other side of the lens.
The image formed by a spherical mirror is real, inverted and is of magnification -2. If the image is at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Find the focal length of the mirror. List two characteristics of the image formed if the object is moved 10 cm towards the mirror.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 50 cm from the mirror.
(a) Write the type of mirror.
(b) Find the distance of the image from the object.
(c) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(d) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
A student has obtained an image of a distant object on a screen to determine the focal length F1 of the given lens. His teacher, after checking the image, gave him another lens of focal length F2 and asked him to focus the same object on the same screen. The student found that to obtain a sharp image, he has to move the lens away from the screen. From this finding, we may conclude that both the lenses given to the student were :
(A) Concave and F1 < F2
(B) Convex and F1 < F2
(C) Convex and F1 > F2
(D) Concave and F1 > F2
A student was asked by his teacher to find the image distance for various object distance in case of a given convex lens. He performed the experiment with all precautions and noted down his observations in the following table:
| S. No. |
Object distance (cm) |
Image distance (cm) |
| 1 | 60 | 15 |
| 2 | 48 | 16 |
| 3 | 36 | 21 |
| 4 | 24 | 24 |
| 5 | 18 | 36 |
| 6 | 16 | 48 |
After checking the observations table the teacher pointed out that there is a mistake in recording the image distance in one of the observations. Find the serial number of the observations having faulty image distance.
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 5
(D) 6
An object is held 20 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Find the position of the image formed.
The image seen in a plane mirror cannot be formed on a screen. What name is given to this type of image?
When an object is placed at a distance of 50 cm from a concave spherical mirror, the magnification produced is, `-1/2`. Where should the object be placed to get a magnification of, `-1/5`?
Linear magnification produced by a concave mirror may be:
(a) less than 1 or equal to 1
(b) more than 1 or equal than 1
(c) less than 1, more than 1 or equal to 1
(d) less than 1 or more than 1
Magnification produced by a convex mirror is always:
(a) more than 1
(b) less than 1
(c) equal to 1
(d) more or less than 1
A concave mirror produces magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a) at the focus
(b) between focus and centre of curvature
(c) between focus and pole
(d) between the centre of curvature
If a magnification of, −1 (minus one) is to be obtained by using a converging mirror, then the object has to be placed:
(a) between pole and focus
(b) at the centre of curvature
(c) beyond the centre of curvature
(d) at infinity
In order to obtain a magnification of, −0.6 (minus 0.6) with a concave mirror, the object must be placed:
(a) at the focus
(b) between pole and focus
(c) between focus and centre of curvature
(d) beyond the centre of curvature
Draw a diagram to show how a converging lens held close to the eye acts as a magnifying glass. Why is it usual to choose a lens of short focal length for this purpose rather than one of long focal length?
Explain what is meant by a virtual, magnified image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual magnified image of an object by a convex lens. In your diagram, the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus should be shown clearly.
The lens A produces a magnification of, − 0.6 whereas lens B produces a magnification of + 0.6.
What is the nature of lens A?
The lens A produces a magnification of, − 0.6 whereas lens B produces a magnification of + 0.6.
What is the nature of lens B?
An object of height 6 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 5 cm. Use lens formula to determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm.
At what distance should an object be placed from a lens of focal length 25 cm to obtain its image on a screen placed on the other side at a distance of 50 cm from the lens? What will be the magnification produced in this case?
Solve the following example.
5 cm high object is placed at a distance of 25 cm from a converging lens of focal length of 10 cm. Determine the position, size and type of the image.
Solve the following example.
An object kept 60 cm from a lens gives a virtual image 20 cm in front of the lens. What is the focal length of the lens? Is it a converging lens or diverging lens?
At which position will you keep an object in front of convex lens to get a real image smaller than the object? Draw a figure.
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance 15 cm from it, at a distance 60 cm in front of it. Find the magnification.
Find the position and magnification of the image of an object placed at distance of 8.0 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 10.0 cm. Is the image erect or inverted?
An object is placed vertically at a distance of 20 cm from a convex lens. If the height of the object is 5 cm and the focal length of the lens is 10 cm, what will be the position, size and nature of the image? How much bigger as compared to the object?
The magnification produced when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a spherical mirror is +1/2. Where should the object be placed to reduce the magnification to +1/3.
The magnification by a lens is -3. Name the lens and state how are u and v related?
What information about the nature of image is erect or inverted, do you get from the sign of magnification + or -?
