Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Boric acid is polymeric due to ______.
पर्याय
its acidic nature
the presence of hydrogen bonds
its monobasic nature
its geometry
उत्तर
Boric acid is polymeric due to the presence of hydrogen bonds.
Explanation:
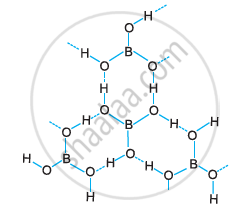
Boric acid is polymeric because of the presence of hydrogen bonds. In the given figure, the dotted lines represent hydrogen bonds.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Is boric acid a protic acid? Explain.
Write a balanced equation for \[\ce{H3BO3 ->[\Delta]}\]?
An aqueous solution of borax is _______.
Explain the Structure of Diborane.
Boric acid is an acid because its molecule ______.
Explain the nature of boric acid as a Lewis acid in water.
Draw the structure of boric acid showing hydrogen bonding. Which species is present in water? What is the hybridisation of boron in this species?
When aqueous solution of borax is acidified with hydrochloric acid, a white crystalline solid is formed which is soapy to touch. Is this solid acidic or basic in nature? Explain.
What are boranes? Give chemical equation for the preparation of diborane.
A compound (A) of boron reacts with NMe3 to give an adduct (B) which on hydrolysis gives a compound (C) and hydrogen gas. Compound (C) is an acid. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Give the reactions involved.
Which is correct statement about diborane structure?
On the addition of mineral acid to an aqueous solution of borax, the compound formed is ______.
Boron reacts with nitric acid to form ______.
Which one of the following methods is used to prepare borax crystals?
Boric acid (H3BO3) is ______.
Borazine, also known as inorganic benzene, can be prepared by the reaction of 3-equivalents of “X” with 6-equivalents of “Y”. “X” and “Y”, respectively are ______.
The reaction of H3N3B3Cl3(A) with LiBH4 in tetrahydrofuran gives inorganic benzene (B). Further, the reaction of (A) with (C) leads to H3N3B3(Me)3. Compounds (B) and (C) respectively, are ______.
