Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Briefly describe the Given structure - Ear
उत्तर
Ear: Ear is the sense organ for hearing and equilibrium. It consists of three portions – external ear, middle ear, and internal ear
1. External ear:
It consists of pinna, external auditory meatus, and a tympanic membrane.
(a) Pinna is a sensitive structure that collects and directs the vibrations into the ear to produce sound.
(b) External auditory meatus is a tubular passage supported by cartilage in external ear.
(c) Tympanic membrane is a thin membrane that lies close to the auditory canal. It separates the middle ear from external ear.
2. Middle ear:
It is an air-filled tympanic cavity that is connected with pharynx through eustachian tube. Eustachian tube helps to equalize air pressure in both sides of tympanic membrane. The middle ear contains a flexible chain of three middle bones called ear ossicles. The three ear ossicles are malleus, incus, and stapes that are attached to each other.
3. Internal ear:
It is also known as labyrinth. Labyrinth is divided into bony labyrinth and a membranous labyrinth. Bony labyrinth is filled with perilymph while membranous labyrinth is filled with endolymph. Membranous labyrinth is divided into 2 parts.
(a) Vestibular apparatus
Vestibular apparatus is a central sac-like part that is divided into utriculus and sacculus. A special group of sensory cells called macula are present in sacculus and utriculus.
Vestibular apparatus also contains three semi-circular canals. The lower end of each semi-circular canal contains a projecting ridge called crista ampularis. Each ampulla has a group of sensory cells called crista. Crista and macula are responsible for maintaining the balance of body and posture.
(b) Cochlea:
Cochlea is a long and coiled outgrowth of sacculus. It is the main hearing organ. Cochlea consists of three membranes. The organ of corti, a hearing organ, is located on the basilar membrane that has hair cells.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Briefly describe the structure of the Brain.
Briefly describe the Given structure - Eye
Compare the following:
Central neural system (CNS) and Peripheral neural system (PNS)
Explain the following process:
Polarisation of the membrane of a nerve fibre
Explain the following process:
Depolarisation of the membrane of a nerve fibre.
Write short note on the following:
Neural coordination
Distinguish between Afferent neurons and efferent neurons.
Examine the diagram of the two cell types A and B given below and select the correct option.
The respiratory centre is present in the ______.
The abundant intracellular cation is ______.
Several statements are given here in reference to cone cells which of the following option indicates all correct statements for cone cells?
Statements
- Cone cells are less sensitive in bright light than Rod cells
- They are responsible for colour vision
- Erythropsin is a photo pigment which is sensitive to red colour light
- They are present in fovea of retina
Which of the following statement concerning the somatic division of the peripheral neural system is incorrect?
The choroid plexus secretes cerebrospinal fluid. List the function of it.
What is ANS? Explain the components of ANS.
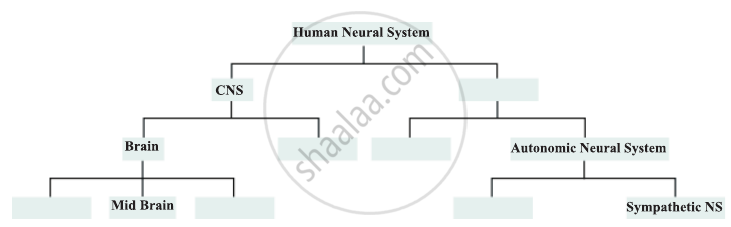
The major parts of the human neural system is depicted below. Fill in the empty boxes with appropriate words.
Neural system and computers share certain common features. Comment in five lines. (Hint: CPU, input-output devices).
