Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Briefly explain the elementary particles present in nature.
उत्तर
- An atom has a nucleus surrounded by electrons and the nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. Till 1960s, it was thought that protons, neutrons and electrons are fundamental building blocks of matter.
- In 1964, physicists Murray Gellman and George Zweig theoretically proposed that protons and neutrons are not fundamental particles; in fact they are made up of quarks. These quarks are now considered elementary particles of nature. Electrons are fundamental or elementary particles because they are not made up of anything.
- In the year 1968, the quarks were discovered experimentally by Stanford Linear Accelerator Centre (SLAC), USA. There are six quarks namely, up, down, charm, strange, top and bottom and their antiparticles. All these quarks have fractional charges.
For example, a charge of up quark is +`2/3`e and that of down quark is - `1/3`e. - According to the quark model, a proton is made up of two up quarks and one down quark, and a neutron is made up of one up quark and two down quarks.
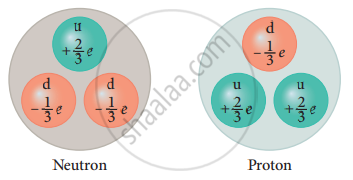
Constituents of nucleons - The study of elementary particles is called particle physics and it is an active area of research even now.
- Till date, more than 20 Nobel prizes have been awarded in the field of particle physics.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate the energy in fusion reaction:
`""_1^2H+_1^2H->_2^3He+n`, where BE of `""_1^2H`23He=7.73MeV" data-mce-style="position: relative;">=2.2323He=7.73MeV MeV and of `""_2^3He=7.73 MeV`
Write notes on Nuclear fission
Write notes on Nuclear fusion
Explain the processes of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion by using the plot of binding energy per nucleon (BE/A) versus the mass number A
Free 238U nuclei kept in a train emit alpha particles. When the train is stationary and a uranium nucleus decays, a passenger measures that the separation between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus becomes x in time t after the decay. If a decay takes place when the train is moving at a uniform speed v, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger will be
Show that the minimum energy needed to separate a proton from a nucleus with Zprotons and N neutrons is `ΔE = (M_(Z-1,N) + M_B - M_(Z,N))c^2`
where MZ,N = mass of an atom with Z protons and N neutrons in the nucleus and MB = mass of a hydrogen atom. This energy is known as proton-separation energy.
Calculate the Q-values of the following fusion reactions :-
(a) `""_1^2H + ""_1^2H → ""_1^3H + ""_1^1H`
(b) `""_1^2H + ""_1^2H → ""_2^3H + n`
(c) `""_1^2H + ""_1^3H → _2^4H + n`.
Atomic masses are `m(""_1^2H) = 2.014102 "u", m(""_1^3H) = 3.016049 "u", m(""_2^3He) = 3.016029 "u", m(""_2^4He) = 4.002603 "u".`
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
Write one balanced reaction representing nuclear fusion.
Explain in detail the four fundamental forces in nature.
The curve of binding energy per nucleon as a function of atomic mass number has a sharp peak for helium nucleus. This implies that helium nucleus is ______.
