Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Briefly mention the contribution of T.H. Morgan in genetics.
उत्तर
Thomas Hunt Morgan (1866-1945), an American geneticist and Nobel Prize winner in 1933, is recognised as the "Father of Experimental Genetics" for his work on and discovery of linkage, crossing over, sex linkage, criss-cross inheritance, linkage maps, gene mutability, and so on. He is known as the fly man of genetics because he used fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) as research subjects in experimental genetics. Genetics was mainly acknowledged as a unique discipline of biology as a result of his book "The Theory of Gene". In 1910, he identified linkage and discriminated between linked and unlinked genes. Morgan and Castle's (1911) "Chromosomal Theory of Linkage" argued that genes are located on chromosomes and ordered in linear order. Morgan and Sturtevant (1911) discovered that the frequency of crossover (recombination) between two connected genes is exactly proportional to their distance. 1% recombination is equivalent to 1 centi Morgan (cM) or 1 map unit. He researched on sex-linked inheritance and discovered a white-eyed male Drosophila in a red-eyed population, proving that the gene for eye colour is situated on the X-chromosome. The man passed genes on X-chromosomes to the daughter, whereas the son receives genes on X-chromosomes from the mother. It is known as criss-cross inheritance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If centromere is situated in the middle of the chromosome, it is called ________.
(a) Metacentric
(b) Acrocentric
(c) Submetacentric
(d) Telocentric
Define the term ‘genome’.
Classify the chromosomes on the basis of position of centromere.
Choose the correct options of the following question:
Study the given monohybrid cross:
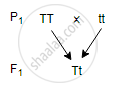
A test cross for this Fj will be:
Explain codominance in colour coat in cattle with checker board method.
Match the column I (Type of chromosome) with column II (name of chromosome).
| Type of chromosome | Name of chromosome | ||
| i. |  |
P. | Acrocentric |
| ii. |  |
Q. | Telocentric |
| iii. |  |
R. | Metacentric |
| iv. |  |
S. | Sub-metacentric |
Which of the following is a primary constriction?
From the following identify the INCORRECT statement/s with respect to the chromosomes.
i. Chromosomes are capable of self replication and play vital role in heredity, mutation, variation, and evolutionary development of eukaryotic species.
ii. Chromosomes are visible during cell division.
iii. Chemically eukaryotic chromosomes are made of mRNA, histone and non-histone proteins.
iv. The number of chromosomes varies within the population of a particular species.
From the following identify the statements that are CORRECT with respect to homologous and non-homologous region of X and Y chromosomes.
i. Non-homologous region of X chromosome is longer and contains more genes than that of non-homologous region of Y chromosome.
ii. X-linked genes are present on nonhomologous region of X-chromosome.
iii. Y-linked genes are present on homologous region of Y-chromosome.
iv. Crossing over occurs only between homologous regions of X and Y chromosomes.
Which of the following does NOT agree with chrotnosomal theory of inheritance?
A plant having the genotype AABbCC will produce ______ kinds of gametes.
Extra nuclear chromosomes occur in ______.
Extranuclear inheritance is a consequence of presence of genes in ______.
Two or more independent genes present on different chromosomes which determine nearly same phenotype are called ______.
Mendel’s work was rediscovered by three scientists in the year ______.
What do you mean by locus?
Experimental verification of the chromosomal theory of inheritance was done by ______.
A haemophilic man marries a carrier woman and they have a daughter. What is the probability of their daughter being haemophilic?
