Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate National Income using Income method and Output method.
| PARTICULARS | (₹ crores) | |
| (i) | Value of output | 1200 |
| (ii) | Wages and salaries | 165 |
| (iii) | Rent | 60 |
| (iv) | Subsidies | 15 |
| (v) | Mixed Income of self employed | 180 |
| (vi) | Employer's contribution to social security | 15 |
| (vii) | Value of intermediate consumption | 600 |
| (viii) | Interest | 7 |
| (ix) | Factor income earned from abroad | 15 |
| (x) | Indirect taxes | 90 |
| (xi) | Profits | 23 |
| (xii) | Depreciation | 75 |
| (xiii) | Factor income paid abroad | 30 |
उत्तर
Income Method:
NDPFC Compensation to employees + Operating Surplus + Mixed Income
= (165 + 15) + (60 + 7 + 23) + 180
= 450
NNFFC = NDPFC + NFIA
= 450 + (−15)
= 435 crores
Output method:
GVA = GDPMP
= Value of output − Value of Intermediate Consumption
= 1,200 − 600
= 600 crores
NNPFC = GDPMP − Depreciation + NFIA − NIT
= 600 − 75 + (−15) − (90 − 15)
= 435 crores
The National Income calculated using the Income method is ₹ 435 crores, while the Output method is also ₹ 435 crores.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given normal income, how can we find real income? Explain.
Explain non-monetary exchanges as a limitation of using the gross domestic product as an index of the welfare of a country
“Income method” is also known as ______.
From the following data, calculate Personal Income and Personal Disposable Income.
| Rs (crore) | ||
| (a) | Net Domestic Product at factor cost | 8,000 |
| (b) | Net Factor Income from abroad | 200 |
| (c) | Undisbursed Profit | 1,000 |
| (d) | Corporate Tax | 500 |
| (e) | Interest Received by Households | 1,500 |
| (f) | Interest Paid by Households | 1,200 |
| (g) | Transfer Income | 300 |
| (h) | Personal Tax | 500 |
Identify the correctly matched pair of items in Column A to those in Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Income Tax | (a) Forced Transfer |
| 2. Services of Housewives | (b) Market Activities |
| 3. Retirement Pension | (c) Taxable for Firm |
| 4. Annual value of goods and services produced. | (d) Income method |
With a rise in real national income, welfare of the people ______
In an economy, C = 300 + 0.5Y and I = ? 600/- (where C =consumption, Y =income or investment). Compute the equilibrium level of income
Suppose C = 40 + 0.8Y D. T = 50, I = 60, G = 40, X = 90, M = 50 + 0.05Y. Find equilibrium income
Suppose C = 40 + 0.8Y D. T = 50, I = 60, G = 40, X = 90, M = 50 + 0.05Y. Find the net export balance at equilibrium income
In the above question 15, if exports change to X = 100, find the change in equilibrium income
______ is the part of Profit.
If in an economy the value of Net Factor Income from Abroad is ₹200 crores and the value of Factor Income to Abroad is ₹40 crores. Identify the value of Factor Income from Abroad:
What is the other name for Income Method?
Read the following figure carefully and choose the correct pair from the alternatives given below:

Distinguish between Factor Cost and Market Price.
Find the odd word out:
Transfer payments:
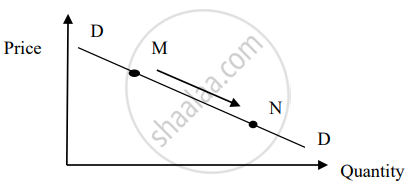
With reference to the diagram shown above, select the reason for the movement from point M to N from the following options.
