Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate National Income using Income method and Output method.
| PARTICULARS | (₹ crores) | |
| (i) | Value of output | 1200 |
| (ii) | Wages and salaries | 165 |
| (iii) | Rent | 60 |
| (iv) | Subsidies | 15 |
| (v) | Mixed Income of self employed | 180 |
| (vi) | Employer's contribution to social security | 15 |
| (vii) | Value of intermediate consumption | 600 |
| (viii) | Interest | 7 |
| (ix) | Factor income earned from abroad | 15 |
| (x) | Indirect taxes | 90 |
| (xi) | Profits | 23 |
| (xii) | Depreciation | 75 |
| (xiii) | Factor income paid abroad | 30 |
उत्तर
Income Method:
NDPFC Compensation to employees + Operating Surplus + Mixed Income
= (165 + 15) + (60 + 7 + 23) + 180
= 450
NNFFC = NDPFC + NFIA
= 450 + (−15)
= 435 crores
Output method:
GVA = GDPMP
= Value of output − Value of Intermediate Consumption
= 1,200 − 600
= 600 crores
NNPFC = GDPMP − Depreciation + NFIA − NIT
= 600 − 75 + (−15) − (90 − 15)
= 435 crores
The National Income calculated using the Income method is ₹ 435 crores, while the Output method is also ₹ 435 crores.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given normal income, how can we find real income? Explain.
Explain non-monetary exchanges as a limitation of using the gross domestic product as an index of the welfare of a country
State which one of the following is true.
From the following data, calculate Personal Income and Personal Disposable Income.
| Rs (crore) | ||
| (a) | Net Domestic Product at factor cost | 8,000 |
| (b) | Net Factor Income from abroad | 200 |
| (c) | Undisbursed Profit | 1,000 |
| (d) | Corporate Tax | 500 |
| (e) | Interest Received by Households | 1,500 |
| (f) | Interest Paid by Households | 1,200 |
| (g) | Transfer Income | 300 |
| (h) | Personal Tax | 500 |
Identify the correctly matched pair of items in Column A to those in Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Income Tax | (a) Forced Transfer |
| 2. Services of Housewives | (b) Market Activities |
| 3. Retirement Pension | (c) Taxable for Firm |
| 4. Annual value of goods and services produced. | (d) Income method |
With a rise in real national income, welfare of the people ______
In an economy, C = 300 + 0.5Y and I = ?. 600/- (where C = consumption, Y = income or investment). Computer the Consumption expenditure at equilibrium level of income
Suppose C = 40 + 0.8Y D. T = 50, I = 60, G = 40, X = 90, M = 50 + 0.05Y. Find equilibrium income
Suppose C = 40 + 0.8Y D. T = 50, I = 60, G = 40, X = 90, M = 50 + 0.05Y. What happens to equilibrium income and the net export balance when the government purchases increase from 40 to 50?
Suppose C = 100 + 0.75Y D, I= 500, G = 750, taxes are 20 per cent of income, X = 150, M = 100 + 0.2Y. Calculate equilibrium income.
______ is the part of Profit.
How is the interest earned by normal resident treated?
If in an economy the value of Net Factor Income from Abroad is ₹200 crores and the value of Factor Income to Abroad is ₹40 crores. Identify the value of Factor Income from Abroad:
What is the other name for Income Method?
Read the following figure carefully and choose the correct pair from the alternatives given below:

Distinguish between Factor Cost and Market Price.
Explain the precautions to be taken while using the income method of measuring national income.
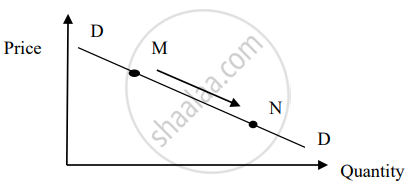
With reference to the diagram shown above, select the reason for the movement from point M to N from the following options.
