Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the resistance of a copper wire 1.0 km long and 0.50 mm diameter if the resistivity of copper is 1.7 × 10−8 Ω m.
उत्तर
Length of the cable wire, l = 1 km = 1000 m
Diameter of the cable wire, d = 0.5 mm
Area of cross-section,
A `= "A"pi^2`
`= 3.14xx(2.5xx10^-4)^2`
`= 0.96xx10^(-8)m^2`
To find the resistance of the copper cable,
We know that `"R"="l"/"A"`
R `= (1.7xx10^-8xx1000)/(19.6xx10^-8)`
So, R = 86.73 Ω
Thus, the resistance of the copper wire, R = 86.73 Ω
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A copper wire has diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity of 1.6 × 10−8Ω m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance 10 Ω? How much does the resistance change if the diameter is doubled?
Which of the following are conductors and which are insulators?
Sulphur, Silver, Copper, Cotton, Aluminium, Air, Nichrome, Graphite, Paper, porcelain, Mercury, Mica, Bakelite, Polythene, Manganin.
What is the general name of the substances having infinitely high electrical resistance?
A wire is 1.0 m long, 0.2 mm in diameter and has a resistance of 10 Ω. Calculate the resistivity of its material?
What would be the effect on the resistance of a metal wire of:
increasing its diameter?
Calculate the area of cross-section of a wire if its length is 1.0 m, its resistance is 23 Ω and the resistivity of the material of the wire is 1.84 × 10−6 Ω m.
The figure blow shows a variable resistor in a dimmer switch.
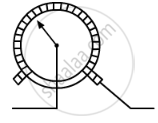
How would you turn the switch to make the lights: (a) brighter, and (b) dimmer? Explain your answer.
Use the data in the Table given below to answer the following –
Which material is the best conductor?
Table give below Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C
| Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C | ||
| − | Material | Resistivity (Ω m) |
| Conductors |
Silver | 1.60 × 10−8 |
| Copper | 1.62 × 10−8 | |
| Aluminium | 2.63 × 10−8 | |
| Tungsten | 5.20 × 10−8 | |
| Nickel | 6.84 × 10−8 | |
| Iron | 10.0 × 10−8 | |
| Chromium | 12.9 × 10−8 | |
| Mercury | 94.0 × 10−8 | |
| Manganese | 1.84 × 10−6 | |
| Alloys |
Constantan (alloy of Cu and Ni) |
49 × 10−6 |
| Manganin (alloy of Cu, Mn and Ni) |
44 × 10−6 | |
| Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe) |
100 × 10−6 | |
| Insulators | Glass | 1010 − 1014 |
| Hard rubber | 1013 − 1016 | |
| Ebonite | 1015 − 1017 | |
| Diamond | 1012 − 1013 | |
| Paper (dry) | 1012 | |
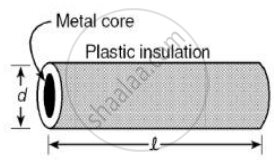
Plastic insulation surrounds a wire having diameter d and length l as shown above. A decrease in the resistance of the wire would be produced by an increase in the ______.
The resistance of a wire of 0.01 cm radius is 10 Ω. If the resistivity of the wire is 50 × 10-8 Ω, find the length of this wire.
