Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits: a 6 V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
उत्तर
As the 6 V battery is connected in series, the potential difference will be different across the two given resistors. So we need the current to calculate the power.
Therefore, the net resistance, R of the circuit
= (1 + 2) Î = 3 Î
Current, `I=V/R=6/3=2A`
Power consumed by the 2-ohm resistor,
P = I2 R
= 22 x 2
= 8 W
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the ratio of potential difference and current known as?
A p.d. of 10 V is needed to make a current of 0.02 A flow through a wire. Wire p.d. is needed to make a current of 250 mA flow through the same wire?
Calculate the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits: a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
What would you suggest to a student if while performing an experiment he finds that the pointer/needle of the ammeter and voltmeter do not coincide with the zero marks on the scales when the circuit is open? No extra ammeter/voltmeter is available in the laboratory.
Three resistors are connected to a 12 V battery as shown in the figure given below:
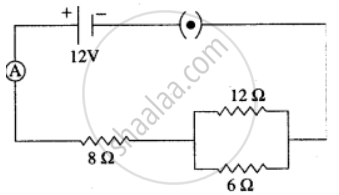
(i) What is the current through the 8 ohm resistor?
(ii) What is the potential difference across the parallel combination of 6 ohm and 12 ohm resistor?
(iii) What is the current through the 6 ohm resistor?
Five resistors of different resistances are connected together as shown in the figure. A 12 V battery is connected to the arrangement.

Calculate:
(i) the total resistance in the circuit
(ii) the total current flowing in the circuit.
Suppose there are three resistors A, B, and C having resistances r1, r2, and r3 respectively. If R represents their equivalent resistance, establish the following relation R = r1 + r2 + r3 when joined in series.
A current of 100 mA. flows through a wire. The charge on an electron is 1.6 × 10-19 C. Find the number of electrons passing per second through the cross-section of the conductor.
Define electric potential and potential difference.
Two charged spherical conductors of radius R1 and R2 are connected by a wire. Then the ratio of surface charge densities of the spheres `(σ_1//σ_2 )` is ______.
