Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the temperature of 4.0 mol of a gas occupying 5 dm3 at 3.32 bar.
(R = 0.083 bar dm3 K–1 mol–1).
उत्तर
Given,
n = 4.0 mol
V = 5 dm3
p = 3.32 bar
R = 0.083 bar dm3 K–1 mol–1
The temperature (T) can be calculated using the ideal gas equation as:
pV = nRT
`=> "T" = ("pV")/("nR")`
`= (3.32xx 5)/(4xx0.083)`
= 50 K
Hence, the required temperature is 50 K.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
34.05 mL of phosphorus vapour weighs 0.0625 g at 546 °C and 0.1 bar pressure. What is the molar mass of phosphorus?
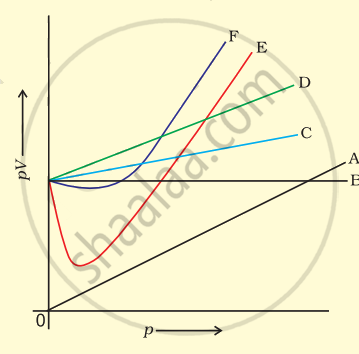
Which curve in figure represents the curve of ideal gas?
The relation between pressure exerted by an ideal gas (Pideal) and observed pressure (Preal) is given by the equation
Pideal = Preal + `(an^2)/V^2`
If pressure is taken in Nm–2, number of moles in mol and volume in m3, Calculate the unit of ‘a’. What will be the unit of ‘a’ when pressure is in atmosphere and volume in dm3?
