Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can Lα X-ray of one material have shorter wavelength than Kα X-ray of another?
उत्तर
An Lα X-ray is emitted when an electron jumps from the M to the L shell, and a Kα X-ray is emitted when an electron jumps from the L to the K shell. Less energy is involved when an electron jumps from the M to the L shell than when it jumps from the L to the K shell. Also, wavelength of a photon is inversely related to its energy. Therefore, an Lα X-ray has higher wavelength than a Kα X-ray for the same material.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are microwaves considered suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation?
How are infrared waves produced?
Arrange the following radiations in the order of their increasing wavelength:
X-rays, infrared rays, ratio waves, gamma ray and microwaves.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with the ultraviolet rays.
Name the waves produced by the changes in the nucleus of an atom.
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively.
- Name the two waves.
- Compare the speeds of these waves when they travel in vacuum.
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in radar systems?
Moseley's Law for characteristic X-ray is √v = a(Z − b). Here,
Heat at the rate of 200 W is produced in an X-ray tube operating at 20 kV. Find the current in the circuit. Assume that only a small fraction of the kinetic energy of electrons is converted into X-rays.
A free atom of iron emits Kα X-rays of energy 6.4 keV. Calculate the recoil kinetic energy of the atom. Mass of an iron atom = 9.3 × 10−26 kg.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
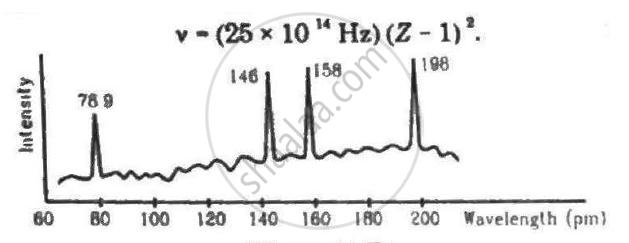
Continuous X-rays are made to strike a tissue paper soaked with polluted water. The incoming X-rays excite the atoms of the sample by knocking out the electrons from the inner shells. Characteristic X-rays are analysed and the intensity is plotted against the wavelength. Assuming that only Kα intensities are detected, list the elements present in the sample from the plot. Use Moseley's equation v − (25 × 1014Hz)(Z − 1)2.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered Ultraviolet rays
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
Produced by bombarding a metal target with high electrons.
State three properties of infrared radiations similar to that of visible light.
Answer briefly.
Give two uses of ultraviolet rays.
Answer briefly.
What are radio waves?
Solve the numerical problem.
Calculate the frequency in MHz of a radio wave of wavelength 250 m. Remember that the speed of all EM waves in a vacuum is 3.0 × 108 m/s.
Find the photon energy in units of ev for electromagnetic wave if waves length 40 m. Given h = 6.63 × 10–34 J.
Radio waves of constant amplitude can be generated with.
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 100 W bulb at a 3 m distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 50 W bulb at the same distance is ______.
