Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Compare the ionising powers of α, β and γ radiations.
उत्तर
The ionising power of α-radiation is nearly 100 times that of β radiations and nearly 10,000 times that of γ-radiations.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The diagram in figure shows a radioactive source S placed in a thick lead walled container. The radiations given out are allowed to pass through a magnetic field. The magnetic field (shown as ×) acts perpendicular to the plane of paper inwards. Arrows shows the paths of the radiation A, B and C.
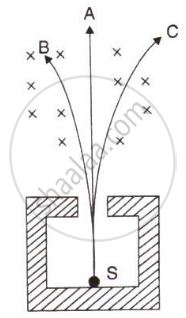
- Name the radiations labelled A, B and C.
- Explain clearly how you used the diagram to arrive at the answer in part (a).
In following Figure shows a mixed source R of alpha and beta particles in a thick lead walled container. The particles pass through a magnetic field in a direction perpendicular to the plane of paper inwards as shown by ×.
- Show in the diagram how the particles get affected.
- Name the law used in part (a).
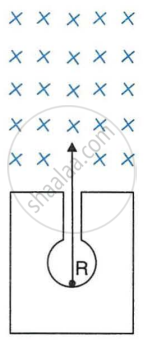
[Hint: Alpha particles will deflect to the left while beta particles to the right]
In following Figure shows a radioactive source S in a thick lead walled container having a narrow opening. The radiations pass through an electric field between the plates A and B.
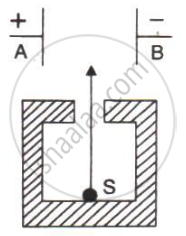
- Complete the diagram to show the paths of α, β and γ radiations.
- Why is the source S kept in a thick lead walled container with a narrow opening?
- Name the radiation which is unaffected by the electrostatic field.
- Which radiation is defleced the most. Given reason.
- Which among the three radiations causes the least biological damage?
Is it possible to deflect γ - radiations in a way similar to α and β -particles, using the electric or magnetic field? Give reasons.
Arrange the α, β, and γ raditions in ascending order of their ionising powers.
What is the composition of α, β and γ radiations?
What are α-and β-radiations?
A beam of α, β and γ rays is travelling through a certain region in space.
- Arrange them in ascending order of ionising power.
- Which of the above will pass undeviated if subjected to an electric field?
- With respect to your answer to part (b) above, what will be the change in the nucleus of an atom after such a ray is emitted.
Which nuclear radiation will travel undeviated in an electric field?
Arrange the α, β and γ radiations in ascending order of their penetrating power.
