Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Compare the ionising powers of α, β and γ radiations.
उत्तर
The ionising power of α-radiation is nearly 100 times that of β radiations and nearly 10,000 times that of γ-radiations.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A radioactive source emits three types of radiations.
Name the radiations which are deflected by the electric field.
In following Figure shows a radioactive source S in a thick lead walled container having a narrow opening. The radiations pass through an electric field between the plates A and B.
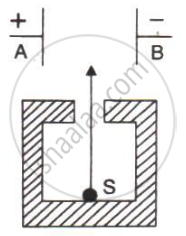
- Complete the diagram to show the paths of α, β and γ radiations.
- Why is the source S kept in a thick lead walled container with a narrow opening?
- Name the radiation which is unaffected by the electrostatic field.
- Which radiation is defleced the most. Given reason.
- Which among the three radiations causes the least biological damage?
Explain why alpha and beta particles are deflected in an electric or a magnetic field, but gamma rays are not deflected in such a field.
Is it possible to deflect γ - radiations in a way similar to α and β -particles, using the electric or magnetic field? Give reasons.
State following four properties each of α, β and γ radiations:
- Nature,
- Charge,
- Mass and
- Effect of electric field.
What is the composition of α, β and γ radiations?
What are α-and β-radiations?
The figure shows a radioactive source S placed in a thick-walled lead container. The radiations given off pass through a magnetic field acting in direction perpendicular to the plane of paper inwards as shown by X. Copy the diagram and show the path of radiations. Explain why the source is kept in a thick-walled lead container.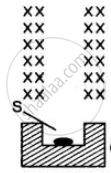
A beam of α, β and γ rays is travelling through a certain region in space.
- Arrange them in ascending order of ionising power.
- Which of the above will pass undeviated if subjected to an electric field?
- With respect to your answer to part (b) above, what will be the change in the nucleus of an atom after such a ray is emitted.
Arrange the α, β and γ radiations in ascending order of their penetrating power.
