Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define current sensitivity of a galvanometer.
उत्तर
Current sensitivity of a galvanometer is defined as the deflection produced in the galvanometer when a unit current flows through it.
θ = `("nBA")/"k""I"`
So, for a given value of I, θ will be large if `("nBA")/"k"` is large i.e n, B and A should be large and k should be small.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the current flowing through a moving coil galvanometer is directly proportional to the angle of deflection of coil.
Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
Explain how moving coil galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter. Derive the necessary formula.
A galvanometer has a resistance of 16Ω. It shows full scale deflection, when a current of 20 mA is passed through it. The only shunt resistance available is 0.06 which is not appropriate to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter. How much resistance should be connected in series with the coil of galvanometer, so that the range of ammeter is 8 A?
Why is it necessary to introduce a radial magnetic field inside the coil of a galvanometer?
Write current sensitivity of a galvanomete S.I. unit.
A galvanometer having a coil resistance of 60 Ω shows full-scale deflection when a current of 1.0 amp passes through it. It can be converted into an ammeter to read currents up to 5.0 amp by:
In an ammeter 0.5% of main current passes through galvanometer; If resistance of galvanometer is G, the resistance of ammeter will be.
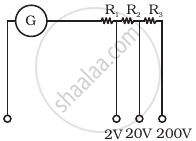
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
To convert a moving coil galvanometer into an ammeter we need to connect a ______.
