Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define ecological pyramids.
उत्तर
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of various environmental parameters, such as the number of individuals present at each trophic level, the amount of energy, or the biomass present at each trophic level. Ecological pyramids represent producers at the base, while the apex represents the top-level consumers present in the ecosystem.
संबंधित प्रश्न
“It is often said that the pyramid of energy is always upright. On the other hand, the pyramid of biomass can be both upright and inverted.” Explain with the help if examples and sketches.
Why the pyramid of energy is always upright? Explain.
In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is _________ type.
Distinguish between Upright and inverted pyramid.
“The pyramid of biomass is not always upright.” Explain the statement.
With reference to the levels of an organisation, differentiate between living organisms and non-living objects.
Answer the following question.
Write any two limitations of ecological pyramids.
Explain with the help of labelled diagrams, the difference between an upright pyramid of biomass and an inverted pyramid of biomass.
Secondary consumers are __________.
Distinguish between the upright and inverted pyramid of biomass.
Which ecosystem has the maximum biomass?
Pyramid of energy in grassland and pond ecosystem is always ______.
Which one of the following is not used for construction of ecological pyramids?
In a pyramid of biomass, if the total dry weight (kgm-2) of primary produces is about 809, it well increases at tertiary consumer level up to ______.
Pyramid of numbers is ______.
Organisms at a higher trophic level have less energy available. Comment.
What are the shortcomings of ecological pyramids in the study of ecosystem?
Write a short note on pyramid of numbers and pyramid of biomass.
(a) Given below is a pyramid of biomass in an ecosystem where each bar represents the standing crop available in the trophic level. With the help of an example explain the conditions where this kind of pyramid is possible in nature.
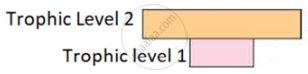
(b) Will the pyramid of energy be also of the same shape in this situation? Give a reason for your response.
Draw a diagram of pyramid of energy.
The biomass of a standing crop of phytoplankton is 4 kg/m2, which supports a large standing crop of zooplankton having a biomass of 11 kg/m2. This is consumed by small fishes having a biomass of 25 kg/m2, which are then consumed by large fishes with a biomass of 37 kg/m2.
Draw an ecological pyramid indicating the biomass at each stage and also name the trophic levels. Mention whether it is an upright or inverted pyramid.
Give scientific reasons:
The pyramid of energy is always upright.
Describe pyramid of energy with the help of diagram.
