Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define a functional group with two examples. write the Functional groups for
(i) Alcohol
(ii) Ketone
(iii) Carboxylic acid
उत्तर
A functional group may be defined as an atom or group of atoms present in a molecule which largely determines its chemical properties.
For Example: -OH- Alcohol, -CHO- Aldehyde
Functional group of:
(i) Alcohol: -OH
(ii) Ketone: >C=O
(iii) Carboxylic acid: -COOH
संबंधित प्रश्न
The equation for the reaction when compound A is bubbled through bromine dissolved in carbon tetrachloride is as follows:
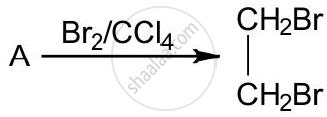
1) Draw the structure of A.
2) State your observation during this reaction.
Name an organic compound which is used for making a household plastic material.
What is the difference in molecular formula of any Two adjacement homologues in terms of types of atoms and molecular mass?
What are addition reactions? How are addition reactions of ethene different
from ethyne?
What word is used to describe theses three compounds taken together?
Ethanol can be converted to ethene which can be changed to ethane.
Choose the correct word or phrase from the options given below to complete the following sentences:
The conversion of ethene to ethane is an example of ________(Hydration, hydrogenation).
Name the gases which extinguishes burning wooden splinter.
Name the gas which: Affects the acidified K2Cr2O7 paper and also turns lime water dirty milky.
Draw the structural diagram for the following compound.
2,2 dibromo butane
The structures of six organic compounds are shown:
|
A \[\begin{array}{cc} |
B \[\begin{array}{cc} |
C \[\begin{array}{cc} |
|
D \[\begin{array}{cc} |
E \[\begin{array}{cc} |
F \[\begin{array}{cc} |
- Identify two of the compounds that are members of the same homologous series but are not isomers.
- Which two compounds are isomers of each other?
- F can be prepared from D. Give a chemical equation for the reaction.
