Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the term polarization of a dielectric and write the expression for a linear isotropic dielectric in terms of electric field.
उत्तर १
Net dipole moment per unit volume induced in dielectric is called polarization. It is represented by P.
P = χeE
P = Polarisation
χe → Electrical succeptibility
E = External electric field.
उत्तर २
Dipole moment per unit volume of a polarized dielectric is known as the polarization of a dielectric. It is denoted by the letter P for the linear isotropic dielectric.
The polarisation of a linear isotropic dielectric,`"P" = "x"epsilon_@"E"`
Where E is the net electric field from the effects of both free and bound charges.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Electric intensity due to a charged sphere at a point outside the sphere decreases with...................
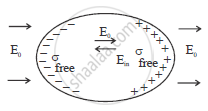
Distinguish with the help of a suitable diagram, the difference in the behaviour of a conductor and a dielectric placed in an external electric field.
How does polarised dielectric modify the original external field?
A dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of an isolated charged capacitor. Which of the following quantities will remain the same?
A dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of a capacitor. The charge on the capacitor is Q and the magnitude of the induced charge on each surface of the dielectric is Q'.
A capacitor stores 50 µC charge when connected across a battery. When the gap between the plates is filled with a dielectric, a charge of 100 µC flows through the battery. Find the dielectric constant of the material inserted.
A parallel-plate capacitor having plate area 400 cm2 and separation between the plates 1⋅0 mm is connected to a power supply of 100 V. A dielectric slab of thickness 0⋅5 mm and dielectric constant 5⋅0 is inserted into the gap. (a) Find the increase in electrostatic energy. (b) If the power supply is now disconnected and the dielectric slab is taken out, find the further increase in energy. (c) Why does the energy increase in inserting the slab as well as in taking it out?
Explain briefly, using a proper diagram, the difference in behaviour of a conductor and a dielectric in the presence of external electric field.
Two metal spheres, one of radius R and the other of radius 2R, both have same surface charge density σ. They are brought in contact and separated. What will be new surface charge densities on them?
The voltage rating of a parallel plate capacitor is 500V. Its dielectric can withstand a maximum electric field of 106 V/m. The plate area is 10-4 m2. What is the dielectric constant if the capacitance is 15 pF?
(given ε0 = 8.86 × 10-12 C2/Nm2)
