Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive the relationship between the peak and the rms value of current in an a.c. circuit.
उत्तर
The instantaneous power dissipated in the resistor is`p = i^2 R = i_m^2 sin^2 omegat`
The average value of p over a cycle is:
`p = <i^2R> =<i_m^2 R sin^2 omegat>`
`i_m^2 and R` are constants. Therefore,
`p = i_m^2 R<sin^2 omegat>`
By trigonometric identity,
`sin^2 omegat = 1/2 (1-cos2 omegat)`
Then,
`<sin^2 omegat > =1/2 (1- <cos2omegat>)`
The average value of cos 2 ωt is zero.
We have:
`< sin^2 omegat > =1/2 (1-0)`
`< sin^2 omegat> =1/2`
Thus,
`P = 1/2 i_m^2`
The rms value in the ac power is expressed in the same form as dc power root mean square or effective current and is denoted by Irms.
Peak current is `i_m`
Therefore,
`I = (i_m)/sqrt2 =0.707 i_m`
`I^2 R = (i_m^2)/2 R`
`I = i_m/sqrt2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define electric resonance.
Define capacitive reactance. Give its units.
Calculate the instantaneous value at 60°, average value and RMS value of an alternating current whose peak value is 20 A.
Why is choke coil needed in the use of fluorescent tubes with ac mains? Why can we not use an ordinary resistor instead of the choke coil?
The phase relationship between current and voltage in a pure resistive circuit is best represented by ______.
For a series LCR circuit, I vs ω curve is shown:
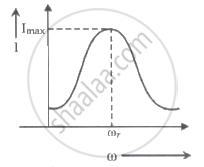
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly capacitive.
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly inductive.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is equal to the resistance of the circuit.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is 0.
An inductor of 0.5 mH, a capacitor of 200 µF, and a resistor of 2Ω are connected in series with a 220V ac source. If the current is in phase with the emf, the frequency of ac source will be ______ × 102 Hz.
A direct current of 4 A and an alternating current of peak value 4 A flow through resistance of 3Ω and 2Ω respectively. The ratio of heat produced in the two resistances in same interval of time will be ______.
State any one difference between a direct current (dc) and an alternating current (ac).
