Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the adsorption theory of catalysis.
उत्तर
Langmuir explained the action of catalysts in heterogeneous catalysed reactions based on adsorption. The reactant molecules are adsorbed on the catalyst surfaces, so this can also be called contact catalysis.
According to this theory, the reactants are adsorbed on the catalyst surface to form an activated complex which subsequently decomposes and gives the product.
The various steps involved in heterogeneous catalysed reactions are given as follows:
- Reactant molecules diffuse from bulk to the catalyst surface.
- The reactant molecules are adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst.
- The adsorbed reactant molecules are activated and form an activated complex which is decomposed to form the products.
- The product molecules are desorbed.
- The product diffuses away from the surface of the catalyst.
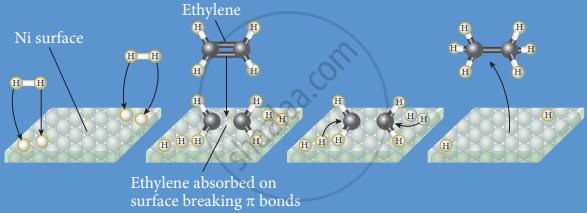
Hydrogenation of ethylene in presence of a nickel catalyst
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term Inhibition.
Define the term Catalysis.
In the reaction, \[\ce{H2O2_{(aq)} ->[I^-_{( aq)}] H2O_{(l)} + \frac{1}{2} O2_{(g)}}\] iodide ion acts as ____________.
Which of the following is the INCORRECT match?
Which one of the following is an example for homogeneous catalysis?
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| A) Pure nitrogen | (i) Chlorine |
| B) Haber process | (ii) Sulphuric acid |
| C) Contact process | (iii) Ammonia |
| D) Deacons Process | (iv) sodium azide (or) Barium azide |
Which of the following is the correct option?
What are enzymes?
What is the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis?
Zeigler-Natta Catalyst is ______.
In preparation of sulphuric acid from sulphur dioxide in lead chamber process. What substance is used as a catalyst?
