Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe the adsorption theory of catalysis.
Solution
Langmuir explained the action of catalysts in heterogeneous catalysed reactions based on adsorption. The reactant molecules are adsorbed on the catalyst surfaces, so this can also be called contact catalysis.
According to this theory, the reactants are adsorbed on the catalyst surface to form an activated complex which subsequently decomposes and gives the product.
The various steps involved in heterogeneous catalysed reactions are given as follows:
- Reactant molecules diffuse from bulk to the catalyst surface.
- The reactant molecules are adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst.
- The adsorbed reactant molecules are activated and form an activated complex which is decomposed to form the products.
- The product molecules are desorbed.
- The product diffuses away from the surface of the catalyst.
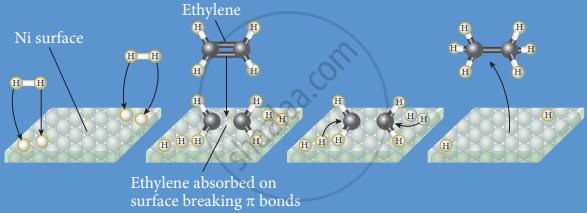
Hydrogenation of ethylene in presence of a nickel catalyst
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the term Inhibition.
Define the term Catalysis.
171 g of sucrose on hydrolysis gives ____________ mole(s) of glucose.
(Atomic wt: C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
What are enzymes?
Write a brief note on the mechanism of enzyme catalysis.
Write a note on catalytic poison.
Explain the intermediate compound formation theory of catalysis with an example.
What is the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis?
Zeigler-Natta Catalyst is ______.
Match List - I with List - II.
| List - I | List - II | ||
| (Processes/Reactions) | (Catalyst) | ||
| (A) | \[\ce{2SO2(g) + O2(g) -> 2SO3(g)}\] | (I) | Fe(s) |
| (B) | \[\ce{4NH3 (g) + 5O2(g) -> 4NO(g) + 6H2O (g)}\] | (II) | Pt (s) - Rh (s) |
| (C) | \[\ce{N2(g) + 3H2(g) -> 2NH3(g)}\] | (III) | V2O5 |
| (D) | \[\ce{Vegetable oil (l) + H2 -> Vegetable ghee (s)}\] | (IV) | Ni (s) |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
