Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe simple experiments to show the presence of -
oxygen and nitrogen component in air using a bell jar
उत्तर
Oxygen and nitrogen in air:
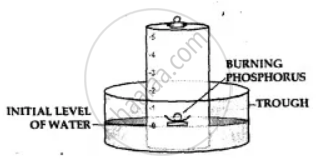
Apparatus— A through, a bell jar, a cork and a crucible and a piece of white phosphorus.
producer-
- The trough is filled with water and a bell jar divided into 5 equal parts, ‘1 to 5’ is placed over it.
- A crucible containing white phosphorus is placed on a cork which is made to float on water.
- The level of the water inside and outside are adjusted to one level.
- The phosphorus is then ignited by means of a heated wire.
Observation-
- The phosphorus burns in the active component of air [oxygen] forming – dense white fumes of phosphorus pentoxide [P2O5]. Phosphorus + Oxygen →Phosphorus pentoxide
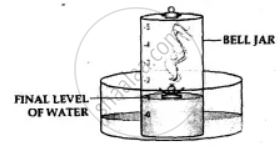
- The level of the water in the bell jar rises by l/5th.
Conclusion-
- Oxygen— The active component of air, i.e. 1/5th of air, is used up in burning.
- Nitrogen— The inactive component of air, i.e. 4/ 5 of air, is not used up in burning. Hence air contains oxygen which supports combustion and nitrogen which does not.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A mixture of oxygen and carbon dioxide used for artificial respiration.
What happens when potassium nitrate is heated ?
Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ in front of following statement.
The rust formed on the surface of iron easily crumbles.
How will you prove that oxide formed by burning sodium is basic in nature?
State two most important conditions for rusting.
Describe simple experiments to show the presence of -
carbon dioxide in air using a test tube with outlets containing lime water.
Describe simple experiments to show the presence of -
water vapour in air using a glass tumbler and ice.
In the laboratory preparation of oxygen from hydrogen peroxide answer the following:
State the word equation for the reaction involving the above preparation of oxygen.
Name the following:
The gas required for both combustion and rusting.
Match the following
| 1. | Burning of meteors | a. | Exosphere |
| 2. | Weather change | b. | Stratosphere |
| 3. | Lowest temperature | c. | Mesosphere |
| 4. | Ozone layer | d. | Troposphere |
