Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Differentiate between the Rods and Cones of Retina (Type of pigment)
उत्तर
Rods and Cones of Retina (Type of pigment):
| Rods | Cones |
| Rods produce rhodopsin. | Cones produce iodopsin. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain how the human ear works.
Lightning and thunder take place in the sky at the same time and at the same distance from us. Lightning is seen earlier and thunder is heard later. Can you explain?
Given in the box below are a set of 14 biological terms. Of these, 12 can be paired into 6 matching pairs. Out of the six pairs, one has been done for you as an example.
Example : endosmosis - Turgid cell.
Identify the remaining five matching pairs :
| Cushing’s syndrome, Turgid cell, Iris, Free of rod and cone cells, Colour of eyes, Hypoglycemia, Active transport, Acrosome, Addison’s disease, Blind spot, Hyperglycemia, Spermatozoa, Endosmosis, Clotting of blood. |
Give technical terms for The nerve which transmits impulses from the ear to the brain
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). If false, correct them by changing any one single word in each.
Semi-circular canals are concerned with static (positional) balance.
Name the three ear ossicles.
Name the tube which connects the middle ear to throat.
Give the main function of the following:
Cochlea
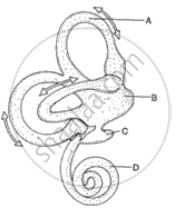
The diagram alongside represents the structure found in the inner ear. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
(ii) Name the parts of the ear responsible for transmitting impulses to the brain.
(iii) Name the part labelled above which is responsible for:
1. Static equilibrium. 2. Dynamic equilibrium. 3. Hearing
(iv) Name the audio receptor cells which pick up vibrations.
(v) Name the fluid present in the inner ear.
Choose the correct answer :
Organ of corti is found in ___________
Differentiate between:
Cochlea and Concha.
The following diagram refers to the ear of a mammal.

(i) Label the parts 1 to 10 to which the guidelines point.
(ii) Which structure:
(a) converts sound waves into mechanical vibrations?
(b) Converts vibrations into nerve impulses?
(c) Responds to change in position?
(d) Transmits impulses to the brain?
(e) Equalizes atmospheric pressure and pressure in the ear.
State the functions of the following:
Semi-circular canals
Choose the Odd One Out:
Mention the name of passage is the outer ear which carries sound waves to the eardrum.
Vibrating particles travel all the way from the vibrating objects to the ear.
The Eardrum moves inward when a rarefaction reaches it.
With reference to human ear answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the ear associated with the amplification of vibrations.
