Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Differentiate between the following -
Dominance and Recessive
उत्तर
| Sr. No. | Dominance | Recessive |
| 1. | The dominant allele may reveal itself even in the presence of the recessive gene. | A recessive allele or factor cannot express its effect in the presence of a dominant allele. |
| 2. | It does not require another similar allele to have an influence on the phenotype; for example, Tt is tall. | It has a phenotypic effect solely in the presence of an equivalent llele, such as tt is dwarf. |
| 3. | Dominant alleles or factors can create full polypeptides or enzymes to express their effects, such as the red colour of pea flowers. | The recessive allele produces an incomplete or faulty polypeptide or enzyme, resulting in the absence of the effect of the dominant allele, such as white flower colour in pea. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between the following -
Monohybrid and Dihybrid.
When a cross in made between tall plant with yellow seeds (TtYy) and tall plant with green seed (Ttyy), what proportions of phenotype in the offspring could be expected to be
- Tall and green.
- Dwarf and green.
How would you find out whether a given tall garden pea plant is homozygous or heterzygous? Substantiate your answer with the help fo Punnett squares.
Answer the following question.
Write the basis on which Alfred Sturtevant explained gene mapping.
A garden pea plant produces axial white flowers. Another of the same species produced terminal violet flowers. Identify the dominant trait?
What do you understand by the terms phenotype and genotype?
Pure-bred tall pea plants are first crossed with pure-bred dwarf pea plants. The pea plants obtained in the F1 generation are then selfed to produce F2 generation of pea plants.
What do the plants of the F1 generation look like?
Pure-bred tall pea plants are first crossed with pure-bred dwarf pea plants. The pea plants obtained in the F1 generation are then selfed to produce F2 generation of pea plants.
Which type of plants was missing in the F1 generation but reappeared in the F2 generation?
Genotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross is ______.
A Monohybrid cross is ______
Punnett square is used to know
In a cross between red coloured and white coloured flowers, when plants with red coloured flowers of F1 generation were self pollinated, plants of F2 generation were obtained in which 75% of plants were with red flowers and 2.5% plants were with white flowers.
Explain the inheritance of traits in the above cross with the help of a flow chart only along with the ratio of plants obtained.
Assertion (A): In humans, if gene (B) is responsible for black eyes and gene (b) responsible for brown eyes, then the colour of eyes of the progeny having gene combination Bb, bb or BB will be black only.
Reason (R): The black colour of the eyes is a dominant trait.
Given below is a schematic representation of the inheritance of the shape of the seeds of garden peas. Answer the questions that follow:
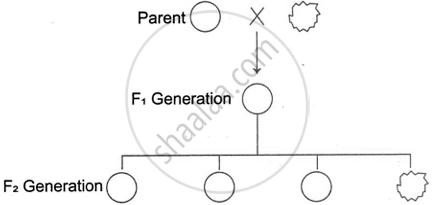
- Which is the dominant and recessive allele of the trait?
- What does the ratio 3 : 1 in the F2 generation represent?
- State Mendel's Law of Dominance.
