Topics
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Flower - a Fascinating Organ of Angiosperms
- Parts of Flower
- Accessory Organs
- Essential Parts of Flower: Androecium
- Essential Parts of Flower: Gynoecium
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pre-fertilisation in Flowering Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Anther
- Transverse Section of Mature Anther (Microsporangium)
- Microsporogenesis
- Microspores and Pollen Grains
- Development of Male Gametophyte
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Pollen Grains
- Structure of Ovule (Megasporangium)
- Types of Ovules
- Megasporogenesis
- Development of Female Gametophyte or Embryo Sac
- Pollination
- Outbreeding Devices
- Artificial Hybridization
- Kinds of Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Abiotic Agents
- Biotic Agents
- Fertilization Process
- Fertilization Process
- Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Endosperm
- Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny)
- Development of Seed
- Development of Fruit
- Apomixis
- Polyembryony
Reproduction in Organisms
- Life Span of Organisms
- Maximum Life Span of Organisms
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Types of Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Budding
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Fission
- Budding
- Sporulation (Sporogenesis)
- Fragmentation
- Different Phases in Sexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Pre-fertilisation Events in Organisms
- Fertilisation in Organisms
- Post-fertilisation Events in Organisms
Reproduction
Genetics and Evolution
Human Reproduction
Reproductive Health
Biology and Human Welfare
Environmental Issues
- Environmental Issues
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Controlling Vehicular Air Pollution: a Case Study of Delhi
- Introduction of Water Pollution and Its Control
- Effects of Domestic Sewage and Industrial Effluents on Water
- A Case Study of Integrated Waste Water Treatment
- Solid Wastes
- Agrochemicals and Their Effects
- Radioactive Wastes
- Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
- Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
- Degradation by Improper Resource Utilisation and Maintenance
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Radioactive Waste Management and E-waste
- Solid Waste Management
- Noise Pollution
- Environmental Issues
Biotechnology
Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Introduction of Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Mendelism
- Terminology Related to Mendelism
- Mendel’s experiments on pea plant
- Monohybrid Cross
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Punnett Square
- Back Cross and Test Cross
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- The Law of Dominance
- The Law of Segregation (Law of Purity of Gametes)
- The Law of Independent Assortment
- Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Codominance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
- Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Codominance
- Multiple Alleles
- Intragenic Interactions - Pleiotropy
- Polygenic Inheritance
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Historical Development of Chromosome Theory
- Comparison Between Gene and Chromosome Behaviour
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Segregation
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Independent Assortment
- Linkage and Recombination
- Sex Determination
- Sex Determination in Some Insects
- Sex Determination in Human
- Sex Determination in Birds
- Sex Determination in Honey Bees
- Concept of Mutation
- Pedigree Analysis
- Genetic Disorders
- Mendelian Genetics
- Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Heredity and Variation
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Introduction of Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- Structure of Polynucleotide Chain
- Packaging of DNA Helix
- Search for Genetic Material
- Introduction of Search for Genetic Material
- The Genetic Material is a DNA
- Properties of Genetic Material (DNA Versus RNA)
- The RNA World
- DNA Replication
- The Experimental Proof
- The Machinery and the Enzymes
- Protein Synthesis
- Introduction of Transcription
- Transcription Unit
- Transcription Unit and the Gene
- Types of RNA and the Process of Transcription
- Genetic Code
- Genetic Code
- Genetic Code
- tRNA – the Adapter Molecule
- Translation
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Operon Concept
- Human Genome Project
- DNA Fingerprinting Technique
- Structure of DNA and RNA
- Structure of Nucleotide
- Rice Genome Project
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance (Questions)
Ecology
Evolution
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Evolution of Life Forms - a Theory
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Theories of Biological Evolution
- Adaptive Radiation
- Organic Evolution
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Brief Account of Evolution
- Human Evolution
- Darwinism
- Micro and Macro Evolution
- Speciation
- Evolution Stages
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Gene Flow and Genetic Drift
- Evolution
Human Health and Diseases
- Introduction of Human Health and Diseases
- Common Diseases in Human Beings
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Allergies (Hypersensitivity)
- Autoimmunity
- Human Immune System
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Cancer
- Introduction of Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Adolescence - Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- Addiction and Dependence
- Effects of Drug and Alcohol
- Prevention and Control of Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Infectious and Non Infectious Disease
- Maintaining Good Health, Yoga, Excercise
- Human Health and Diseases (Questions)
Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Household Products
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Production of Biogas
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
- Energy Generation
- Production and Judicious Use
- Microbes in Human Welfare
Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Restriction Enzymes
- Cloning Vectors
- Competent Host (For Transformation with Recombinant DNA)
- Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology
Biotechnology and Its Application
Organisms and Populations
- Introduction of Organisms and Populations
- Ecology (Organism, Population, Community and Biome)
- Introduction of Organisms and Environment
- Major Abiotic Factors
- Responses to Abiotic Factors
- Population Attributes
- Population Growth
- Life History Variation
- Population Interactions
- Population and Ecological Adaptations
- Organisms and Populations (Questions)
Ecosystem
- Ecosystem
- Introduction and Types of Ecosystem
- Structure and Function of an Ecosystem
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Ecological Pyramids
- Ecological Succession
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecosystem Services
- Ecosystems Patterns
Biodiversity and Its Conservation
- Biodiversity
- Species on Earth and Species in India
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Importance of Species Diversity to the Ecosystem
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Biodiversity
- Endangered Organisms
- Importance of Biodiversity
- Extinction
- Red Data Book
- Biodiversity and Its Conservation (Questions)
- Monohybrid Cross
- Representation of a Gene
Monohybrid Cross:
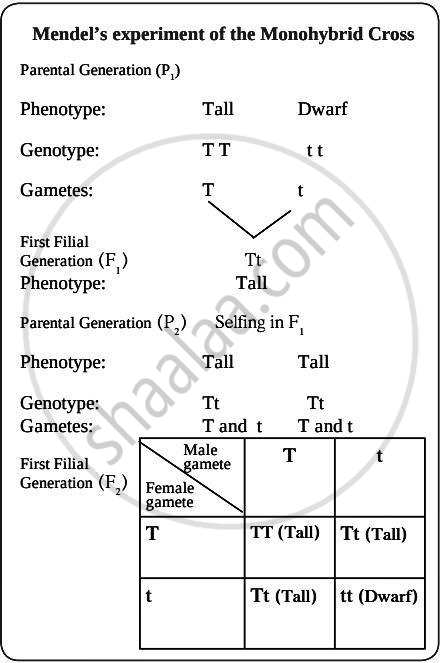
In this experiment, Mendel brought about the cross between two pea plants with only one pair of contrasting characters. This type of cross is called a monohybrid cross. To study the monohybrid ratio, let us consider the characteristic ‘plant height’ with a pair of contrasting characteristics: tall plant and dwarf plant.
- The Tt plant is heterozygous for genes controlling one character (height); it is a monohybrid and the cross between TT and tt is a monohybrid cross.
- When a pure tall pea plant (TT) produces gametes by meiosis, each gamete has the allele 'T'. Similarly, when a pure dwarf pea plant (tt) produces gametes by meiosis, each gamete has the allele 't.'
- During fertilisation, the two alleles, 'T' from one parent, say through the pollen, and t from the other parent, then through the egg, are united to produce zygotes that have one T allele and one t allele. In other words, the hybrids have Tt.
- Since these hybrids contain alleles that express contrasting traits, the plants are heterozygous.
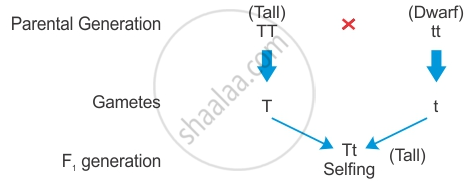
In the F2 generation, when F1 plants are self-pollinated, the recessive trait reappears.
This is because the recessive parental trait is expressed without any blending in the F2 generation. While during gamete formation, these alleles segregate and each gamete receives only one allele from each pair of factors. This segregation of alleles is a random process and so there is a 50% chance of a gamete containing either allele.
For example:
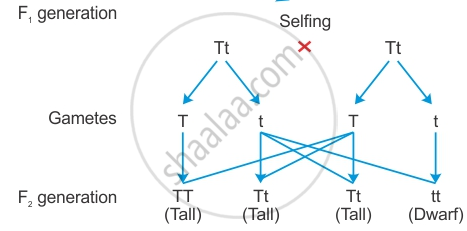
When fertilisation takes place, pollen grains with genotype 'T' have a 50% chance to pollinate eggs with genotype 'T' as well as genotype 't'. Similarly, pollen grains with genotype 't' have a 50% chance to pollinate eggs with genotype 'T,' as well as of genotype 't'. As a result of random fertilisation, resultant zygotes formed by selfing of the F1 generation have genotypes TT, Tt, or tt. (TT: pure tall, Tt: hybrid tall, tt: dwarf).
| F₂ Pure dominant (TT): tall plants | Homozygous |
|---|---|
| F₂ Pure recessive (tt): dwarf plants | Homozygous |
| F₂ Hybrid plants (Tt): tall plants | Heterozygous |

Monohybrid cross
Phenotypic ratio: 3 (tall): 1 (dwarf)
Genotypic ratio: 1 (TT): 2 (Tt): 1 (tt).
Representation of a Gene:
Generally, a gene is represented by alphabetical symbols. The capital letter is used for the trait expressed at the F1 stage, and the small alphabet for the other trait. For example, in the case of the character of height, "T" is used for the tall trait and 't' for the ‘dwarf." Both T and t are alleles of each other. Hence, in plants, the pair of alleles for height would be TT, Tt, or tt.
- Mendel also proposed that in a true-breeding, tall or dwarf pea variety, the allelic pair of genes for height are identical or homozygous, TT and tt, respectively.
- When an individual has dissimilar alleles (Tt) for a particular trait, it is known as 'heterozygous' or 'hybrid' for a specific trait.
- Thus, the genetic constitution for a particular trait (i.e., 'TT,' Tt, or 'tt') is known as the 'genotype,' and the type of character it represents (i.e., tallness and dwarfness) is known as the 'phenotype.'
- As Mendel found the phenotype of the F1 heterozygote Tt to be exactly like the TT parent in appearance, he proposed that in a pair of dissimilar factors, one dominates the other (as in the F1) and hence is called the dominant factor while the other factor is recessive. For example, T (for tallness) is dominant over t (for dwarfness), which is recessive.
- It is convenient to use the capital and lowercase of an alphabetical symbol to remember this concept of dominance and recessiveness.
