Topics
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Flower - a Fascinating Organ of Angiosperms
- Parts of Flower
- Accessory Organs
- Essential Parts of Flower: Androecium
- Essential Parts of Flower: Gynoecium
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pre-fertilisation in Flowering Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Anther
- Transverse Section of Mature Anther (Microsporangium)
- Microsporogenesis
- Microspores and Pollen Grains
- Development of Male Gametophyte
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Pollen Grains
- Structure of Ovule (Megasporangium)
- Types of Ovules
- Megasporogenesis
- Development of Female Gametophyte or Embryo Sac
- Pollination
- Outbreeding Devices
- Artificial Hybridization
- Kinds of Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Abiotic Agents
- Biotic Agents
- Fertilization Process
- Fertilization Process
- Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Endosperm
- Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny)
- Development of Seed
- Development of Fruit
- Apomixis
- Polyembryony
Reproduction in Organisms
- Life Span of Organisms
- Maximum Life Span of Organisms
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Types of Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Budding
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Fission
- Budding
- Sporulation (Sporogenesis)
- Fragmentation
- Different Phases in Sexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Pre-fertilisation Events in Organisms
- Fertilisation in Organisms
- Post-fertilisation Events in Organisms
Reproduction
Genetics and Evolution
Human Reproduction
Reproductive Health
Biology and Human Welfare
Environmental Issues
- Environmental Issues
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Controlling Vehicular Air Pollution: a Case Study of Delhi
- Introduction of Water Pollution and Its Control
- Effects of Domestic Sewage and Industrial Effluents on Water
- A Case Study of Integrated Waste Water Treatment
- Solid Wastes
- Agrochemicals and Their Effects
- Radioactive Wastes
- Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
- Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
- Degradation by Improper Resource Utilisation and Maintenance
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Radioactive Waste Management and E-waste
- Solid Waste Management
- Noise Pollution
- Environmental Issues
Biotechnology
Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Introduction of Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Mendelism
- Terminology Related to Mendelism
- Mendel’s experiments on pea plant
- Monohybrid Cross
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Punnett Square
- Back Cross and Test Cross
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- The Law of Dominance
- The Law of Segregation (Law of Purity of Gametes)
- The Law of Independent Assortment
- Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Codominance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
- Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Codominance
- Multiple Alleles
- Intragenic Interactions - Pleiotropy
- Polygenic Inheritance
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Historical Development of Chromosome Theory
- Comparison Between Gene and Chromosome Behaviour
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Segregation
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Independent Assortment
- Linkage and Recombination
- Sex Determination
- Sex Determination in Some Insects
- Sex Determination in Human
- Sex Determination in Birds
- Sex Determination in Honey Bees
- Concept of Mutation
- Pedigree Analysis
- Genetic Disorders
- Mendelian Genetics
- Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Heredity and Variation
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Introduction of Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- Structure of Polynucleotide Chain
- Packaging of DNA Helix
- Search for Genetic Material
- Introduction of Search for Genetic Material
- The Genetic Material is a DNA
- Properties of Genetic Material (DNA Versus RNA)
- The RNA World
- DNA Replication
- The Experimental Proof
- The Machinery and the Enzymes
- Protein Synthesis
- Introduction of Transcription
- Transcription Unit
- Transcription Unit and the Gene
- Types of RNA and the Process of Transcription
- Genetic Code
- Genetic Code
- Genetic Code
- tRNA – the Adapter Molecule
- Translation
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Operon Concept
- Human Genome Project
- DNA Fingerprinting Technique
- Structure of DNA and RNA
- Structure of Nucleotide
- Rice Genome Project
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance (Questions)
Ecology
Evolution
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Evolution of Life Forms - a Theory
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Theories of Biological Evolution
- Adaptive Radiation
- Organic Evolution
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Brief Account of Evolution
- Human Evolution
- Darwinism
- Micro and Macro Evolution
- Speciation
- Evolution Stages
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Gene Flow and Genetic Drift
- Evolution
Human Health and Diseases
- Introduction of Human Health and Diseases
- Common Diseases in Human Beings
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Allergies (Hypersensitivity)
- Autoimmunity
- Human Immune System
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Cancer
- Introduction of Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Adolescence - Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- Addiction and Dependence
- Effects of Drug and Alcohol
- Prevention and Control of Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Infectious and Non Infectious Disease
- Maintaining Good Health, Yoga, Excercise
- Human Health and Diseases (Questions)
Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Household Products
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Production of Biogas
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
- Energy Generation
- Production and Judicious Use
- Microbes in Human Welfare
Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Restriction Enzymes
- Cloning Vectors
- Competent Host (For Transformation with Recombinant DNA)
- Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology
Biotechnology and Its Application
Organisms and Populations
- Introduction of Organisms and Populations
- Ecology (Organism, Population, Community and Biome)
- Introduction of Organisms and Environment
- Major Abiotic Factors
- Responses to Abiotic Factors
- Population Attributes
- Population Growth
- Life History Variation
- Population Interactions
- Population and Ecological Adaptations
- Organisms and Populations (Questions)
Ecosystem
- Ecosystem
- Introduction and Types of Ecosystem
- Ecosystem - Structure and Function
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Ecological Pyramids
- Ecological Succession
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecosystem Services
- Ecosystems Patterns
Biodiversity and Its Conservation
- Biodiversity
- Species on Earth and Species in India
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Importance of Species Diversity to the Ecosystem
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Biodiversity
- Endangered Organisms
- Importance of Biodiversity
- Extinction
- Red Data Book
- Biodiversity and Its Conservation (Questions)
- Androecium: Male Reproductive Organ
- Male reproductive unit: Stamen
- Fusion of Stamens
- Anther types
- Anther attachment
Notes
Androecium: The male reproductive organ
Male reproductive unit: Stamen
- The third whorl of flowers is the male reproductive part of the flower.
- It is composed of stamens (microsporophylls).
- A stamen is an angiosperm's male reproductive unit.
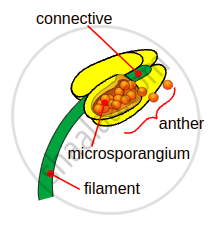
- A typical stamen differentiates into three parts - Filament, Anther, and Connective.
 Structure of Stamen |
- Filament - The long and slender stalk is called the filament. The proximal end of the filament is attached to the thalamus or the petal of the flower.
- Anther - The anther is a bilobed structure with each lobe containing four pollen sacs or microsporangia. Anther typically contains two compartments called thecae (singular theca). Each theca consists of two microsporangia. Two microsporangia fused to form a locule.
- Connective - Anther and filament are attached together with the help of a small region, called connective. Connective contains vascular tissues.
- Sterile stamens are called Staminodes. Example: Cassia.
(i) Distinct: stamens which do not fuse to one another.
(i) Free: stamens which do not fuse with other parts of flower.
(iii) Apostemonous: flowers with stamens that are free and distinct.
Notes
Fusion of Stamens:
- The fusion of stamens fusing among themselves or with other parts of flower.
- They are of two types - Connation and Adnation
1) Connation: Refers to the fusion of stamens among themselves. It is of 3 types - Adelphy, Syngenecious, and Synandrous.
- Adelphy: Filaments connate into one or more bundles but anthers are free. It may be the following types.
(i) Monadelphous: Filaments of stamens connate into a single bundle. Example: Malvaceae (China rose, Cotton).

Monadelphous
(ii) Diadelphous: Filaments of stamens connate into two bundles. Example: Fabaceae (pea) and Clitoria.
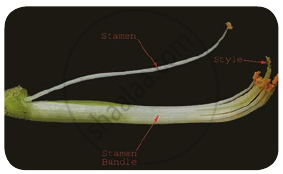
Diadelphous
(iii) Polyadelphous: Filaments connate into many bundles. Example: Citrus, Bombax

Polyadelphous
- Syngenesious: Anthers connate, filaments free. Example: Asteraceae.
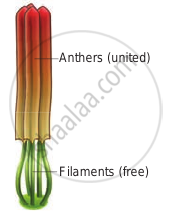
Syngenesious
- Synandrous: Filaments and anthers are completely fused. Example: Coccinea.
2) Adnation: Refers to the fusion of stamens with other floral parts.
- Epipetalous: Stamens are adnate to petals. Example: brinjal, Datura.
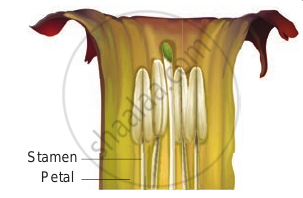
Epipetalous
- Episepalous: stamens are adnate to sepals. Example: Grevillea (Silver oak)
- Epitepalous (epiphyllous): stamens are adnate to tepals. Example: Asparagus.
- Gynostegium: Connation product of stamens and stigma is called gynostegium. Example: Calotropis and Orchidaceae.
- Pollinium: Pollen grains are fused together as a single mass. Example: Calotropis
Notes
Arrangement of stamens relate to length of stamens:
- Didynamous: Four stamens of which two with long filaments and two with short filaments. Example: Ocimum
- Tetradynamous: Six stamens of which four with long filaments and two with short filaments. Example: Brassica.
- Heterostemonous: stamens are of different lengths in the same flower. Example: Cassia.
Notes
Anther types:
- Monothecal: One lobe with two microsporangia. They are kidney-shaped in a cross-section. Example: Malvaceae

Monothecal
- Dithecal: It is a typical type, having two lobes with four microsporangia. They are butterfly-shaped in cross-section. Example: Solanaceae.

Dithecal
Notes
Anther attachment:
- Basifixed: (Innate) Base of anther is attached to the tip of filament. Example: Datura.
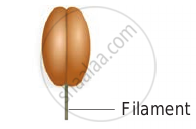
Basifixed - Dorsifixed: Apex of filament is attached to the dorsal side of the anther. Example: Hibiscus.

Dorsifixed - Versatile: Filament is attached to the anther at midpoint. Example: Grasses.
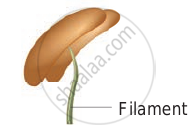
Versatile - Adnate: Filament is continued from the base to the apex of anther. Example: Nelumbo

Adnate
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Video Tutorials
Shaalaa.com | Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant
to track your progress
