Topics
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Flower - a Fascinating Organ of Angiosperms
- Parts of Flower
- Accessory Organs
- Essential Parts of Flower: Androecium
- Essential Parts of Flower: Gynoecium
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pre-fertilisation in Flowering Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Anther
- Transverse Section of Mature Anther (Microsporangium)
- Microsporogenesis
- Microspores and Pollen Grains
- Development of Male Gametophyte
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Pollen Grains
- Structure of Ovule (Megasporangium)
- Types of Ovules
- Megasporogenesis
- Development of Female Gametophyte or Embryo Sac
- Pollination
- Outbreeding Devices
- Artificial Hybridization
- Kinds of Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Abiotic Agents
- Biotic Agents
- Fertilization Process
- Fertilization Process
- Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Endosperm
- Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny)
- Development of Seed
- Development of Fruit
- Apomixis
- Polyembryony
Reproduction in Organisms
- Life Span of Organisms
- Maximum Life Span of Organisms
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Types of Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Budding
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Fission
- Budding
- Sporulation (Sporogenesis)
- Fragmentation
- Different Phases in Sexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Pre-fertilisation Events in Organisms
- Fertilisation in Organisms
- Post-fertilisation Events in Organisms
Reproduction
Genetics and Evolution
Human Reproduction
Reproductive Health
Biology and Human Welfare
Environmental Issues
- Environmental Issues
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Controlling Vehicular Air Pollution: a Case Study of Delhi
- Introduction of Water Pollution and Its Control
- Effects of Domestic Sewage and Industrial Effluents on Water
- A Case Study of Integrated Waste Water Treatment
- Solid Wastes
- Agrochemicals and Their Effects
- Radioactive Wastes
- Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
- Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
- Degradation by Improper Resource Utilisation and Maintenance
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Radioactive Waste Management and E-waste
- Solid Waste Management
- Noise Pollution
- Environmental Issues
Biotechnology
Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Introduction of Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Mendelism
- Terminology Related to Mendelism
- Mendel’s experiments on pea plant
- Monohybrid Cross
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Punnett Square
- Back Cross and Test Cross
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- The Law of Dominance
- The Law of Segregation (Law of Purity of Gametes)
- The Law of Independent Assortment
- Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Codominance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
- Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Codominance
- Multiple Alleles
- Intragenic Interactions - Pleiotropy
- Polygenic Inheritance
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Historical Development of Chromosome Theory
- Comparison Between Gene and Chromosome Behaviour
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Segregation
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Independent Assortment
- Linkage and Recombination
- Sex Determination
- Sex Determination in Some Insects
- Sex Determination in Human
- Sex Determination in Birds
- Sex Determination in Honey Bees
- Concept of Mutation
- Pedigree Analysis
- Genetic Disorders
- Mendelian Genetics
- Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Heredity and Variation
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Introduction of Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- Structure of Polynucleotide Chain
- Packaging of DNA Helix
- Search for Genetic Material
- Introduction of Search for Genetic Material
- The Genetic Material is a DNA
- Properties of Genetic Material (DNA Versus RNA)
- The RNA World
- DNA Replication
- The Experimental Proof
- The Machinery and the Enzymes
- Protein Synthesis
- Introduction of Transcription
- Transcription Unit
- Transcription Unit and the Gene
- Types of RNA and the Process of Transcription
- Genetic Code
- Genetic Code
- Genetic Code
- tRNA – the Adapter Molecule
- Translation
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Operon Concept
- Human Genome Project
- DNA Fingerprinting Technique
- Structure of DNA and RNA
- Structure of Nucleotide
- Rice Genome Project
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance (Questions)
Ecology
Evolution
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Evolution of Life Forms - a Theory
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Theories of Biological Evolution
- Adaptive Radiation
- Organic Evolution
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Brief Account of Evolution
- Human Evolution
- Darwinism
- Micro and Macro Evolution
- Speciation
- Evolution Stages
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Gene Flow and Genetic Drift
- Evolution
Human Health and Diseases
- Introduction of Human Health and Diseases
- Common Diseases in Human Beings
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Allergies (Hypersensitivity)
- Autoimmunity
- Human Immune System
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Cancer
- Introduction of Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Adolescence - Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- Addiction and Dependence
- Effects of Drug and Alcohol
- Prevention and Control of Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Infectious and Non Infectious Disease
- Maintaining Good Health, Yoga, Excercise
- Human Health and Diseases (Questions)
Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Household Products
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Production of Biogas
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
- Energy Generation
- Production and Judicious Use
- Microbes in Human Welfare
Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Restriction Enzymes
- Cloning Vectors
- Competent Host (For Transformation with Recombinant DNA)
- Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology
Biotechnology and Its Application
Organisms and Populations
- Introduction of Organisms and Populations
- Ecology (Organism, Population, Community and Biome)
- Introduction of Organisms and Environment
- Major Abiotic Factors
- Responses to Abiotic Factors
- Population Attributes
- Population Growth
- Life History Variation
- Population Interactions
- Population and Ecological Adaptations
- Organisms and Populations (Questions)
Ecosystem
- Ecosystem
- Introduction and Types of Ecosystem
- Ecosystem - Structure and Function
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Ecological Pyramids
- Ecological Succession
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecosystem Services
- Ecosystems Patterns
Biodiversity and Its Conservation
- Biodiversity
- Species on Earth and Species in India
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Importance of Species Diversity to the Ecosystem
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Biodiversity
- Endangered Organisms
- Importance of Biodiversity
- Extinction
- Red Data Book
- Biodiversity and Its Conservation (Questions)
Definition
Parturition: After nine months of pregnancy, the fully developed foetus is ready for delivery. The process of childbirth is called parturition.
Notes
Parturition (process of Birth):
Parturition is triggered via a complex neuroendocrine mechanism. Birth signals come from a fully developed foetus and placenta. These signals cause mild uterine contractions. It is called the foetal excretory reflex. This causes the release of oxytocin from the maternal pituitary gland. Oxytocin acts on the muscles of the uterus, causing stronger contractions. These contractions stimulate further secretion of oxytocin. The stimulatory reflex between uterine contractions and oxytocin secretion continues, resulting in progressively stronger contractions. This causes the baby to be expelled from the womb through the birth canal. After the baby is born, the placenta is also drained from the uterus. Secretion of CRH by the placenta increases enormously toward the end of pregnancy. Women who have higher levels of CRH earlier in pregnancy are more likely to deliver prematurely, whereas those who have low levels are more likely to deliver after their due date. After the birth of the child, the size of the uterus decreases, and its lining is rapidly restored. It takes nearly 6 months to return back to pre-pregnant status).
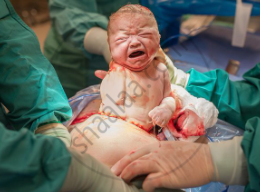 |
Test Tube Babies:
Test tube baby is a technique concerned to a woman who is not able to conceive to give birth to a normal baby. Test tube babies are not developed in a test tube as the name points out. The term ‘test tube’ refers to ‘in-vitro’ or ‘in glass’ where the fertilization of eggs by sperm is carried out. This technology is called in-vitro fertilization (IVF) technology. IVF technology was pioneered in humans by Prof. Robert Winston.
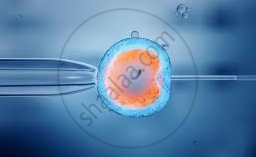 |
Methodology Involves:
- Removal of the unfertilized ovum from the reproductive tract of a female.
- The egg is kept under aseptic conditions.
- Fertilization of eggs in test tubes by sperm (in semen) obtained from males.
- The gametes take about 12-15 hours to fertilize.
- After fertilization, the zygote is transferred into another fluid medium resembling body temperature.
- When the embryo reaches the 32-celled stage, it is implanted into the uterus of another female which serves as the host animal or surrogate mother.
- These host animals or surrogate mothers are used only to serve as animal incubators and to deliver off springs after the normal gestation (pregnancy) period.
- This results in the normal birth of a baby who is called a test tube baby.
- The surrogate mothers don’t contribute anything in terms of genetic makeup since the egg is from the donor mother and semen is from the donor father.
- The First attempt to produce a test tube baby was made by an Italian scientist, Dr. Petrucci (1959 A.D.).
- Subhash Mukherjee created India's first and the world's second test tube baby using in-vitro fertilization.
Definition
Lactation: The mammary glands of the female undergo differentiation during pregnancy and starts producing milk towards the end of pregnancy by the process called lactation.
Notes
Lactation:
The mammary glands of the female undergo differentiation during pregnancy. Lactation is the process by which milk is synthesized and secreted from the mammary glands of the postpartum female breast in response to an infant sucking at the nipple. The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called colostrum. The colostrum contains various antibodies which are absolutely essential to develop resistance for the newborn baby. Breast-feeding during the initial period of infant growth is recommended by doctors for bringing up a healthy baby.
Milk Properties:
- The milk produced during the early stages of lactation differs from the milk produced after maturation, i.e., when lactation is fully established.
- Colostrum is the first milk produced during the first stage of lactation.
- After childbirth, the content of milk gradually changes. Within four to five days of labour, the colostrum transforms into transitional milk.
- Matured milk is produced in the mammary glands 14 to 15 days after childbirth.
Lactation Procedure:
- Breast growth begins throughout pregnancy and continues to increase in size after childbirth due to the influence of ovarian and placental hormones.
- During this time, the breast produces a set amount of milk.
- Only after the baby is born does milk secretion increase.
- Milk is secreted from the mammary glands during the breastfeeding process.
What do you think the doctors inject to induce delivery?
To induce labour pain and delivery, doctors administer oxytocin. The posterior pituitary gland releases oxytocin in response to the foetal ejection reflex, which is begun by a fully formed foetus and placenta. During parturition, oxytocin causes greater uterine contractions (childbirth).
Do you know? What sort of steroids are injected to the mother during pre-mature delivery?
Steroids, commonly known as corticosteroids, are man-made versions of natural human hormones. When pregnant women receive steroid injections, the substance goes through their bloodstream to the baby's body and lungs. A typical "course" of prenatal steroid treatment consists of two injections spaced 24 hours apart. When administered between 25 and 33 weeks of pregnancy, steroids can significantly accelerate the development of the baby's lungs. This improves the chances of survival for many premature newborns.
Text
Do you Know?
-
Varying creatures have different gestation periods. The gestation time for Asian elephants is 617 days, 58-65 days for dogs, and 58-67 days for cats.
- The fusing of male and female gametes results in the formation of a zygote. In humans, the zygote is diploid and has 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes.
