Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Discuss the various types of positive interactions between species.
उत्तर
The interspecific interaction is of three types positive or beneficial, negative or antagonistic and last neutral interaction. Some positive interactions are scavenging, commensalism, protocooperation and mutualism.
Mutualism this interaction confers benefits on both the interacting species, e.g.,
- Lichens represent an intimate mutualistic relationship between a fungus and photosynthesising algae or cyanobacteria.
- The mycorrhizae are associations between fungi and the roots of higher plants. The fungi help the plant in the absorption of essential nutrients from the soil while the plant in turn provides the fungi with energy-yielding carbohydrates.
- Plants offer nectar, juicy and nutritious fruits to animals that help pollinate their flowers and disperse their seeds.
Commensalism This is the interaction in which one species benefits without affecting the other, e.g.,
- An orchid growing as an epiphyte on a mango branch.
- Barnacles growing on the back of a whale.
- The cattle egret goraging close to the cattle that stir up and flush out insects from the vegetation.
- Sea anemone that has stinging tentacles and the clown fish that lives among them to get protection from predators.
Scavenging is the act of feeding by scavengers like bacteria and fungi on the remain of dead animals.
Protocooperation is the type of relationship in which both partners mutually obtain benefits. But they associate purely to benefit from each other and can live without each other.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the role of VAM related to soil fertility.
Name important defense mechanisms in plants against herbivores.
Define mutualism.
Two species competing for the same resources, avoid competition by choosing different times for feeding, also known as ______
Identify the correct pair that exhibits commensalism.
The interspecific interaction between Cuckoo and Crow is ______
Mycorrhizae are the example of ______.
A population has more young individuals compared to the older individuals. What would be the status of the population after some years?
The diagram given below shows the life cycle of a malarial parasite. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follows:
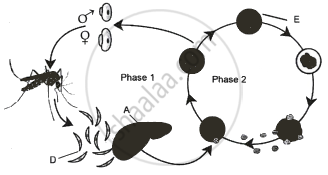
- Name the hosts in which the asexual phase and sexual phase of the life cycle takes place.
- Identify the infective stage labelled ‘D’.
- Name the structure labelled ‘A’ and ‘E’.
- Give any one symptom of malaria.
Give one example of Parasitism.
