Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
3: Human Reproduction
4: Reproductive Health
5: Principle of Inheritance and Variation
6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
7: Evolution
8: Human Health and Diseases
9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
10: Microbes in Human Welfare
11: Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
12: Biotechnology and Its Applications
▶ 13: Organisms and Populations
14: Ecosystem
15: Biodiversity and Conservation
16: Environmental Issues
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 13 - Organisms and Populations NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 13 - Organisms and Populations - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 13: Organisms and Populations
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 13 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Biology [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 13 Organisms and Populations MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS [Pages 88 - 91]
Autecology is ______.
Relation of heterogeneous populations to its environment
Relation of an individual to its environment.
Relation of a community to its environment
Relation of a blame to its environment
Ecotone is ______.
A polluted area
A bottom of a lake
A zone of transition between two communities
A zone of developing community
Biosphere is ______.
A component in the ecosystem
Component of the plants present in the soil
Life in tee outer space
Composed of all living organism present on earth which interact with the physical environment
Ecological niche is ______.
the surface area of the ocean
an ecologically adapted zone
the physical position and functional role of a species within the community
formed of all plants and animals living at the bottom of a lake
According to Allen’s Rule, the mammals from colder climates have ______.
shorter ears and longer limbs
longer ears and shorter limbs
longer ears and longer limbs
shorter ears and shorter limbs
Salt concentration (Salinity) of the sea measured in parts per thousand is ______.
10 – 15
30 – 70
0 – 5
30 – 35
Formation of tropical forests needs mean annual temperature and mean annual precipitation as ______.
18 – 25°C and 150 – 400 cm
5 – 15°C and 50 – 100 cm
30 – 50°C and 100 – 150 cm
5 – 15°C and 100 – 200 cm
Which of the following forest plants controls the light conditions at the ground?
Lianas and climbers
Shrubs
Tall trees
Herbs
What will happen to a well-growing herbaceous plant in the forest if it is transplanted outside the forest in a park?
It will grow normally
It will grow well because it is planted in the same locality
It may not survive because of change in its micro climate
It grows very well because the plant gets more sunlight
If a population of 50 Paramoecium present in a pool increases to 150 after an hour, what would be the growth rate of population?
50 per hour
200 per hour
5 per hour
100 per hour
What would be the per cent growth or birth rate per individual per hour for the same population mentioned in the previous question (Question 10)?
100
200
50
150
A population has more young individuals compared to the older individuals. What would be the status of the population after some years?
It will decline
It will stabilise
It will increase
It will first decline and then stabilise
What parameters are used for tiger census in our country’s national parks and sanctuaries?
Pug marks only
Pug marks and faecal pellets
Faecal pellets only
Actual head counts
Which of the following would necessarily decrease the density of a population in a given habitat?
Natality > mortality
Immigration > emigration
Mortality and emigration
Natality and immigration
A protozoan reproduces by binary fission. What will be the number of protozoans in its population after six generations?
128
24
64
32
In 2005, for each of the 14 million people present in a country, 0.028 were born and 0.008 died during the year. Using exponential equation, the number of people present in 2015 is predicted as ______.
25 millions
17 millions
20 millions
18 millions
Amensalism is an association between two species where ______.
one species is harmed and other is benefitted
one species is harmed and other is unaffected
one species is benefitted and other is unaffected
both the species are harmed
Lichens are association of ______.
bacteria and fungus
alga and bacterium
fungus and alga
fungus and virus
Which of the following is a partial root parasite?
Sandal wood
Mistletoe
Orobanche
Ganoderma
Which one of the following organisms reproduces sexually only once in its lifetime?
Banana
Mango
Tomato
Eucalyptus
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 13 Organisms and Populations VERY SHORT ANSWER [Pages 91 - 92]
Species that can tolerate narrow range of temperature are called ______.
What are Eurythermic species?
Species that can tolerate wide range of salinity are called ______.
Define stenohaline species.
What is the interaction between two species called?
What is commensalism?
Name the association in which one species produces poisonous substance or a change in environmental conditions that is harmful to another species.
What is mycorrhiza?
Emergent land plants that can tolerate the salinities of the sea are called.
Why do high altitude areas have brighter sunlight and lower temperatures as compared to the plains?
What is homeostasis?
Define aestivation.
What is diapause and its significance?
What would be the growth rate pattern, when the resources are unlimited?
What are the organisms that feed on plant sap and other plant parts called?
What is high altitude sickness? Write its symptoms.
What is Commensalism? Explain it with suitable example.
Define ectoparasite and endoparasite and give suitable examples.
What is brood parasitism? Explain with the help of an example.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 13 Organisms and Populations SHORT ANSWER [Pages 92 - 94]
Why are coral reefs not found in the regions from west Bengal to Andhra Pradesh but are found in Tamil Nadu and on the east coast of India?
If a fresh water fish is placed in an aquarium containing sea water, will the fish be able to survive? Explain giving reasons.
Why do all the fresh water organisms have contractile vacuoles whereas majority of marine organisms lack them?
Define heliophytes and sciophytes. Name a plant from your locality that is either heliophyte or sciophyte.
Why do submerged plants receive weaker illumination than exposed floating plants in a lake?
In a sea shore, the benthic animals live in sandy, muddy and rocky substrata and accordingly developed the following adaptations.
Burrowing
Find the suitable substratum against adaptation.
In a sea shore, the benthic animals live in sandy, muddy and rocky substrata and accordingly developed the following adaptations.
Building cubes
Find the suitable substratum against adaptation.
In a sea shore, the benthic animals live in sandy, muddy and rocky substrata and accordingly developed the following adaptations.
Holdfasts/peduncle
Find the suitable substratum against adaptation.
Categorise the following plants into hydrophytes, halophytes, mesophytes and xerophytes. Give reasons for your answers.
Salvinia
Hydrophytes
Halophytes
Mesophytes
Xerophytes
Categorise the following plants into hydrophytes, halophytes, mesophytes and xerophytes. Give reasons for your answers.
Opuntia
Hydrophytes
Halophytes
Mesophytes
Xerophytes
Categorise the following plants into hydrophytes, halophytes, mesophytes and xerophytes. Give reasons for your answers.
Rhizophora
Hydrophytes
Halophytes
Mesophytes
Xerophytes
Categorise the following plants into hydrophytes, halophytes, mesophytes and xerophytes. Give reasons for your answers.
Mangifera
Hydrophytes
Halophytes
Mesophytes
Xerophytes
In a pond, we see plants which are free-floating; rooted–submerged; rooted emergent; rooted with floating leaves; Write the type of plant against the following examples.
| Plant Name | Type | |
| a. | Hydrilla | ______ |
| b. | Typha | ______ |
| c. | Nymphaea | ______ |
| d. | Lemna | ______ |
| e. | Vallisneria | ______ |
The density of a population in a habitat per unit area is measured in different units. Write the unit of measurement against the following:
Bacteria
The density of a population in a habitat per unit area is measured in different units. Write the unit of measurement against the following:
Banyan
The density of a population in a habitat per unit area is measured in different units. Write the unit of measurement against the following:
Deer
The density of a population in a habitat per unit area is measured in different units. Write the unit of measurement against the following:
Fish
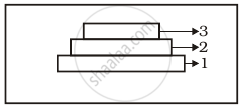
Label the three tiers 1, 2, 3 given in the above age pyramid.
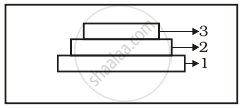
What type of population growth is represented by the above age pyramid?
In an association of two animal species, one is a termite which feeds on wood and the other is a protozoan Trichonympha present in the gut of the termite. What type of association they establish?
Lianas are vascular plants rooted in the ground and maintain erectness of their stem by making use of other trees for support. They do not maintain direct relation with those trees. Discuss the type of association the lianas have with the trees.
Give the scientific names of any two microorganisms inhabiting the human intestine.
What is a tree line?
Define ‘zero population growth rate’. Draw a age pyramid for the same.
List any four characters that are employed in human population census.
Give one example for the following type.
Migratory animal
Give one example for the following type.
Camouflaged animal
Give one example for the following type.
Predator animal
Give one example for the following type.
Biological control agent
Give one example for the following type.
Phytophagous animal
Give one example for the following type.
Chemical defense agent
Fill in the blanks
| Species A | Species B | Type of Interaction | Example |
| + | - | ______ | ______ |
| + | + | ______ | ______ |
| + | 0 | Commensalism | ______ |
Observe the set of 4 figures A, B, C and D and, answer the following questions
- Which one of the figures shows mutualism?
- What kind of association is shown in D?
- Name the organisms and the association in C.
- What role is the insect performing in B?
 Fig. (A) |
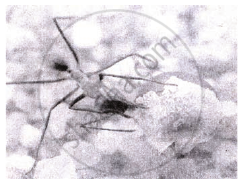 Fig. (B) |
 Fig. (C) |
 Fig. (D) |
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 13 Organisms and Populations LONG ANSWER [Pages 95 - 97]
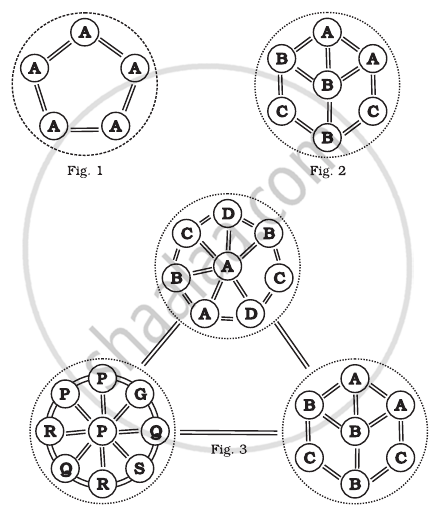
Comment on the following figures: 1, 2 and 3:
A, B, C. D, G, P, Q, R, S are species
An individual and a population has certain characteristics. Name these attributes with definitions.
The following diagrams are the age pyramids of different populations. Comment on the status of these populations.

Comment on the growth curve given below.
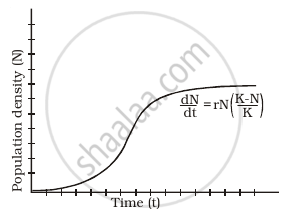
A population of Paramoecium caudatum was grown in a culture medium. After 5 days the culture medium became overcrowed with Paramoeium and had depleted nutrients. What will happen to the population and what type of growth curve will the population attain? Draw the growth curve.
Discuss the various types of positive interactions between species.
In an aquarium two herbivorous species of fish are living together and feeding on phytoplanktons. As per the Gause’s Principle, one of the species is to be eliminated in due course of time, but both are surviving well in the aquarium. Give possible reasons.
While living in and on the host species, the animal parasite has evolved certain adaptations. Describe these adaptations with examples.
Do you agree that regional and local variations exist within each biome? Substantiate your answer with suitable example.
Which element is responsible for causing soil salinity? At what concentration does the soil become saline?
Does light factor affect the distribution of organisms? Write a brief note giving suitable examples of either plants or animals.
Give one example for the following:
Eurythermal plant species
Give one example for the following:
A hot water spring organism
Give one example for the following:
An organism seen in deep ocean trenches
Give one example for the following:
An organism seen in compost pit
Give one example for the following:
A parasitic angiosperm
Give one example for the following:
A stenothermal plant species
Give one example for the following:
Soil organism
Give one example for the following:
A benthic animal
Give one example for the following:
Antifreeze compound seen in antarctic fish
Give one example for the following:
An organism which can conform
Solutions for 13: Organisms and Populations
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 13 - Organisms and Populations NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 13 - Organisms and Populations - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 13 - Organisms and Populations
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE 13 (Organisms and Populations) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 13 Organisms and Populations are Introduction of Organisms and Environment, Population and Ecological Adaptations, Population Interactions, Population Attributes, Responses to Abiotic Factors, Introduction of Organisms and Populations, Ecology (Organism, Population, Community and Biome), Organisms and Populations (Questions), Life History Variation, Major Abiotic Factors, Population Growth.
Using NCERT Exemplar Biology [English] Class 12 solutions Organisms and Populations exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Biology [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 13, Organisms and Populations Biology [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
