Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
3: Human Reproduction
4: Reproductive Health
5: Principle of Inheritance and Variation
▶ 6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
7: Evolution
8: Human Health and Diseases
9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
10: Microbes in Human Welfare
11: Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
12: Biotechnology and Its Applications
13: Organisms and Populations
14: Ecosystem
15: Biodiversity and Conservation
16: Environmental Issues
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Biology [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS [Pages 36 - 40]
In a DNA strand the nucleotides are linked together by ______.
phosphodiester bonds
glycosidic bonds
peptide bonds
hydrogen bonds
A nucleoside differs from a nucleotide. It lacks the ______.
phosphate group
hydroxyl group
sugar
base
Both deoxyribose and ribose belong to a class of sugars called ______.
pentoses
polysaccharides
hexoses
trioses
The fact that a purine base always paired through hydrogen bonds with a pyrimidine base leads to, in the DNA double helix ______.
uniform width throughout DNA
uniform length in all DNA
the semiconservative nature
the antiparallel nature
The net electric charge on DNA and histones is ______.
negative and positive, respectively
both negative
both positive
zero
The promoter site and the terminator site for transcription are located at ______.
5' (upstream) end and 3' (downstream) end, respectively of thetranscription unit
the 5' (upstream) end
the 3' (downstream) end
3' (downstream) end and 5' (upstream) end, respectively of the transcription unit
Which of the following statements is the most appropriate for sickle cell anaemia?
It cannot be treated with iron supplements
It is a molecular disease
It confers resistance to acquiring malaria
All of the above
Which of the following is true with respect to AUG?
It codes for methionine only
It is an initiation codon
It codes for methionine in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
All of the above
The first genetic material could be ______.
RNA
DNA
carbohydrates
protein
With regard to mature mRNA in eukaryotes.
exons appear but introns do not appear in the mature RNA
exons and introns do not appear in the mature RNA
introns appear but exons do not appear in the mature RNA
both exons and introns appear in the mature RNA
The human chromosome with the highest and least number of genes in them are respectively ______.
Chromosome 1 and Y
Chromosome 1 and X
Chromosome X and Y
Chromosome 21 and Y
Who amongst the following scientists had no contribution in the development of the double helix model for the structure of DNA?
Meselson and Stahl
Erwin Chargaff
Maurice Wilkins
Rosalind Franklin
DNA is a polymer of nucleotides which are linked to each other by 3’-5’ phosphodiester bond. To prevent polymerisation of nucleotides, which of the following modifications would you choose?
Remove/Replace 3' OH group in deoxy ribose
Remove/Replace 2' OH group with some other group in deoxy ribose
Both ‘B’ and ‘C’
Replace purine with pyrimidines
Discontinuous synthesis of DNA occurs in one strand, because ______.
DNA dependent DNA polymearse catalyses polymerisation only in one direction (5' → 3')
DNA molecule being synthesised is very long
it is a more efficient process
DNA ligase has to have a role
Which of the following steps in transcription is catalysed by RNA polymerse?
Elongation
Initiation
Termination
All of the above
Control of gene expression in prokaryotes takes place at the level of ______.
Transcription
Translation
DNA-replication
None of the above
Which of the following statements is correct about the role of regulatory proteins in transcription in prokaryotes?
They only increase expression
They only decrease expression
They interact with RNA polymerase but do not affect the expression
They can act both as activators and as repressors
Which was the last human chromosome to be completely sequenced?
Chromosome 1
Chromosome 11
Chromosome 21
Chromosome x
Which of the following are the functions of RNA?
It is a constituent component of ribosomes
It carries amino acids to ribosomes
It is a carrier of genetic information from DNA to ribosomes synthesising polypeptides
All of the above
While analysing the DNA of an organism a total number of 5386 nucleotides were found out of which the proportion of different bases were: Adenine = 29%, Guanine = 17%, Cytosine = 32%, Thymine = 17%. Considering the Chargaff’s rule it can be concluded that ______.
It is single stranded DNA
it is a double stranded circular DNA
It is a double stranded linear DNA
No conclusion can be drawn
In some viruses, DNA is synthesised by using RNA as template. Such a DNA is called ______.
cDNA
rDNA
B-DNA
A-DNA
If Meselson and Stahl's experiment is continued for four generations in bacteria, the ratio of `15_N/15_N:15_N/14_N:14_N/14_N` containing DNA in the fourth generation would be ______.
0 : 1 : 7
0 : 1 : 3
1 : 4 : 0
1 : 1 : 0
If the sequence of nitrogen bases of the coding strand of DNA in a transcription unit is 5' - ATGAATG - 3' the sequence of bases in its RNA transcript would be ______.
5' - AUGAAUG - 3'
5' - UACUUAC - 3'
5' - CAUUCAU - 3'
5' - GUAAGUA - 3'
The RNA polymerase holoenzyme transcribes ______.
the structural gene and the terminator region
the structural gene only
the promoter and the terminator region
the promoter, structural gene, and the terminator region
If the base sequence of a codon in mRNA is 5'-AUG-3', the sequence of tRNA pairing with it must be ______.
5' - CAU - 3'
5' - AUG - 3'
5' - GUA - 3'
5' - UAC - 3'
The amino acid attaches to the tRNA at its ______.
3' - end
5' - end
Anti codon site
DHU loop
To initiate translation, the mRNA first binds to ______.
The smaller ribosomal sub-unit
The larger ribosomal sub-unit
The whole ribosome
No such specificity exists
In E.coli, the lac operon gets switched on when ______.
lactose is present and it binds to the repressor.
repressor binds to operator.
RNA polymerase binds to the operator.
lactose is present and it binds to RNA polymerase.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance VERY SHORT ANSWER [Pages 40 - 41]
What is the function of histones in DNA packaging?
Distinguish between heterochromatin and euchromatin. Which of the two is transcriptionally active?
The enzyme DNA polymerase in E.coli is a DNA dependent polymerase and also has the ability to proof-read the DNA strand being synthesised. Explain. Discuss the dual polymerase.
What is the cause of discontinuous synthesis of DNA on one of the parental strands of DNA? What happens to these short stretches of synthesised DNA?
Given below is the sequence of coding strand of DNA in a transcription unit 3 'A A T G C A G C T A T T A G G – 5’ write the sequence of its complementary strand
Given below is the sequence of coding strand of DNA in a transcription unit 3 'A A T G C A G C T A T T A G G – 5’ write the sequence of the mRNA
What is DNA polymorphism? Why is it important to study it?
Based on your understanding of genetic code, explain the formation of any abnormal hemoglobin molecule. What are the known consequences of such a change?
Sometimes cattle or even human beings give birth to their young ones that are having extremely different sets of organs like limbs/position of eye(s) etc. Comment.
In a nucleus, the number of ribonucleoside triphosphates is 10 times the number of deoxy x10 ribonucleoside triphosphates, but only deoxy ribonucleotides are added during the DNA replication. Suggest a mechanism.
Name a few enzymes involved in DNA replication other than DNA polymerase and ligase. Name the key functions for each of them.
Name any three viruses which have RNA as the genetic material.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance SHORT ANSWER [Pages 41 - 43]
Define transformation in Griffith's experiment. Discuss how it helps in the identification of DNA as the genetic material.
Who revealed biochemical nature of the transforming principle? How was it done?
Discuss the significance of heavy isotope of nitrogen in the Meselson and Stahl’s experiment.
Define a cistron. Giving examples differentiate between monocistronic and polycistronic transcription unit.
Give any six features of the human genome.
During DNA replication, why is it that the entire molecule does not open in one go? Explain replication fork. What are the two functions that the monomers (dNTPs) play?
Retroviruses do not follow central Dogma. Comment.
In an experiment, DNA is treated with a compound which tends to place itself amongst the stacks of nitrogenous base pairs. As a result of which, the distance between two consecutive base increases, from 0.34nm to 0.44 nm. Calculate the length of DNA double helix (which has 2 × 109 bp) in the presence of saturating amount of this compound.
What would happen if histones were to be mutated and made rich in acidic amino acids such as aspartic acid and glutamic acid in place of basic amino acids such as lysine and arginine?
Recall the experiments done by Frederick Griffith, Avery, MacLeod and McCarty, where DNA was speculated to be the genetic material. If RNA, instead of DNA was the genetic material, would the heat killed strain of Pneumococcus have transformed the R-strain into virulent strain? Explain.
You are repeating the Hershey-Chase experiment and are provided with two isotopes: 32P and 15N (in place of 35S in the original experiment). How do you expect your results to be different?
There is only one possible sequence of amino acids when deduced from a given nucleotides. But multiple nucleotides sequence can be deduced from a single amino acid sequence. Explain this phenomena.
A single base mutation in a gene may not ‘always’ result in loss or gain of function. Do you think the statement is correct? Defend your answer.
A low level of expression of lac operon occurs at all the time. Can you explain the logic behind this phenomena.
How has the sequencing of human genome opened new windows for treatment of various genetic disorders. Discuss amongst your classmates.
The total number of genes in humans is far less (< 25,000) than the previous estimate (upto 1,40,000 gene). Comment.
Now, sequencing of total genomes getting is getting less expensive day by the day. Soon it may be affordable for a common man to get his genome sequenced. What in your opinion could be the advantage and disadvantage of this development?
Would it be appropriate to use DNA probes such as VNTR in DNA finger printing of a bacteriaphage?
During in vitro synthesis of DNA, a researcher used 2’, 3’ – dideoxy cytidine triphosphate as raw nucleotide in place of 2’-deoxy cytidine. What would be the consequence?
What background information did Watson and Crick had available with them for developing a model of DNA? What was their own contribution?
What are the functions of methylated guanasine cap?
What are the functions of poly-A “tail” in a mature on RNA?
Do you think that the alternate splicing of exons may enable a structural gene to code for several isoproteins from one and the same gene? If yes, how? If not, why so?
Comment on the utility of variability in number of tandem repeats during DNA finger printing.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance LONG ANSWER [Page 43]
Give an account of Hershey and Chase experiment. What did it conclusively prove? If both DNA and proteins contained phosphorus and sulphur do you think the result would have been the same?
During the course of evolution why DNA was chosen over RNA as genetic material? Give reasons by first discussing the desired criteria in a molecule that can act as genetic material and in the light of biochemical differences between DNA and RNA.
Give an account of post transcriptional modifications of a eukaryotic mRNA.
Discuss the process of translation in detail.
Define an operon. giving an example, explain an Inducible operon.
‘There is a paternity dispute for a child’. Which technique can solve the problem. Discuss the principle involved.
Give an account of the methods used in sequencing the human genome.
List the various markers that are used in DNA finger printing.
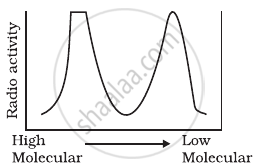
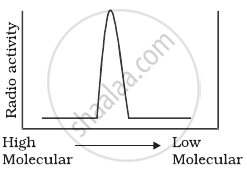
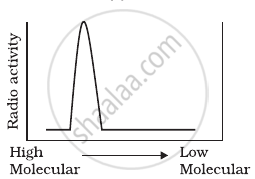
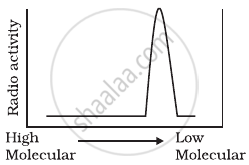
Replication was allowed to take place in the presence of radioactive deoxynucleotides precursors in E.coli that was a mutant for DNA ligase. Newly synthesised radioactive DNA was purified and strands were separated by denaturation. These were centrifuged using density gradient centrifugation. Which of the following would be a correct result?
Solutions for 6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE 6 (Molecular Basis of Inheritance) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance are Packaging of DNA Helix, Introduction of Search for Genetic Material, The Experimental Proof, Introduction of Transcription, Introduction of Molecular Basis of Inheritance, Structure of Nucleotide, Molecular Basis of Inheritance (Questions), Structure of Polynucleotide Chain, The Genetic Material is a DNA, Properties of Genetic Material (DNA Versus RNA), The RNA World, The Machinery and the Enzymes, DNA Replication, Transcription Unit, Transcription Unit and the Gene, Types of RNA and the Process of Transcription, Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure, Search for Genetic Material, Genetic Code, tRNA – the Adapter Molecule, Translation, Regulation of Gene Expression, Human Genome Project, DNA Fingerprinting Technique, Protein Synthesis, Genetic Code, Operon Concept, Structure of DNA and RNA, Rice Genome Project, Genetic Code.
Using NCERT Exemplar Biology [English] Class 12 solutions Molecular Basis of Inheritance exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Biology [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Molecular Basis of Inheritance Biology [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.