Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a pond, we see plants which are free-floating; rooted–submerged; rooted emergent; rooted with floating leaves; Write the type of plant against the following examples.
| Plant Name | Type | |
| a. | Hydrilla | ______ |
| b. | Typha | ______ |
| c. | Nymphaea | ______ |
| d. | Lemna | ______ |
| e. | Vallisneria | ______ |
उत्तर
| Plant Name | Type | |
| a. | Hydrilla | Submerged |
| b. | Typha | Rooted emergent |
| c. | Nymphaea | Rooted with floating leaves |
| d. | Lemna | free – floating |
| e. | Vallisneria | Rooted Submerged |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write what do phytophagous insects feed on.
Select the statement which explains best parasitism.
Name important defense mechanisms in plants against herbivores.
Using '-' to depict inhibition and '+' to depict benefit, mutualism between two species can be represented as ____________.
Which one of the following pair does NOT show commensalism?
An interaction favourable to both population but no obligatory to either is ______.
Define stenohaline species.
The diagram given below shows the life cycle of a malarial parasite. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follows:
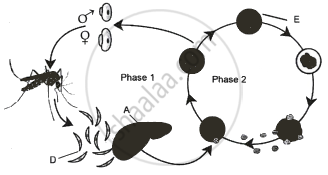
- Name the hosts in which the asexual phase and sexual phase of the life cycle takes place.
- Identify the infective stage labelled ‘D’.
- Name the structure labelled ‘A’ and ‘E’.
- Give any one symptom of malaria.
Describe mutualism.
What happens to an inferior competitor if a superior competitor is present in the same environment?
