Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is Commensalism? Explain it with suitable example.
उत्तर
Commensalism is the interaction between two species in which one species derives benefit and the other one is neither harmed nor benefited.
Commensalism:
- This is the interaction in which one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
- An orchid growing as an epiphyte on a branch of mango tree, will get benefit while the mango tree derives no benefit.
- The cattle egret and grazing cattle in close association, is a classic example of commensalism. Cattle egrets always forage close to cattle, as cattle move they flush out insects that might be difficult for the egrets to find and catch.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the ecological principle behind the biological control method of managing with pest insects?
Answer the following question.
Mention the term used to describe a population interaction between an orchid growing on a forest tree.
Name the type of association: Hummingbirds and host flowering plants
Define the following term:
Camouflage
In Logistic growth curve lag phase shows______.
What is population ecology?
The interaction in nature, where one gets to benefit on the expense of other is _________.
The relationship between sucker fish and shark is _________.
Tabulate and analysis of two species population interaction.
Using '-' to depict inhibition and '+' to depict benefit, mutualism between two species can be represented as ____________.
Statement I: If one or two species are lost, it may not affect proper functioning of ecosystem.
Statement II: Loss of key species causes serious threat to functioning of ecosystem. Choose the correct alternative with reference to the above statements
Type of interspecific interaction wherein one organism is benefited and other is harmed is called ____________.
Exarch xylem is found in:
In an association of two animal species, one is a termite which feeds on wood and the other is a protozoan Trichonympha present in the gut of the termite. What type of association they establish?
Observe the set of 4 figures A, B, C and D and, answer the following questions
- Which one of the figures shows mutualism?
- What kind of association is shown in D?
- Name the organisms and the association in C.
- What role is the insect performing in B?
 Fig. (A) |
 Fig. (B) |
 Fig. (C) |
 Fig. (D) |
Sea Anemone gets attached to the surface of the hermit crab. The kind of population interaction exhibited in this case is ______.
Name any two categories of organisms that in general are adversely affected by competition.
The interaction between cattle egret and the buffalo is ______.
The diagram given below shows the life cycle of a malarial parasite. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follows:
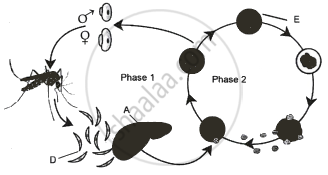
- Name the hosts in which the asexual phase and sexual phase of the life cycle takes place.
- Identify the infective stage labelled ‘D’.
- Name the structure labelled ‘A’ and ‘E’.
- Give any one symptom of malaria.
What happens to an inferior competitor if a superior competitor is present in the same environment?
