Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Tabulate and analysis of two species population interaction.
उत्तर
MUTUALISM (+, +): It is the type of interaction where both species benefit from the interaction. Mutualism may be facultative when the species involved are capable of existence independent of one another, or obligate, when the relationship is imperative of the existence of one or both species.
Examples: i. Certain bacteria in the caeca and intestine of herbivores aid in the digestion of cellulose. ii. The cross pollination of flowers by insects and birds seeking nectar and pollen which is of great importance in agriculture.
COMMENSALISM (+, 0): The concept of commensalism has been broadened in recent years, to apply to coactions other than those centering on food such as cover, support, production, and locomotion.
Examples: i. Barnacles attached to Whales travel thousands of miles collecting and filtering food from the moving water.The whales are not affected by the barnacles. ii. Egrets usually are present near cattle. they catch insects which are disturbed by the cattle.
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is mutualism?
Write what do phytophagous insects feed on.
An orchid plant is growing on the branch of mango tree. How do you describe this interaction between the orchid and the mango tree?
In Logistic growth curve lag phase shows______.
Explain parasitism.
Differentiate between predator and prey.
Statement I: If one or two species are lost, it may not affect proper functioning of ecosystem.
Statement II: Loss of key species causes serious threat to functioning of ecosystem. Choose the correct alternative with reference to the above statements
Identify the interspecific interaction which one species is benefited and other is neither banned nor benefited.
Type of interspecific interaction wherein one organism is benefited and other is harmed is called ____________.
Which population interaction can be represented by'+''-'?
In spite of interspecific competition in nature, which mechanism the competing species might have evolved for their survival?
Amensalism can be represented as ______
In a pond, we see plants which are free-floating; rooted–submerged; rooted emergent; rooted with floating leaves; Write the type of plant against the following examples.
| Plant Name | Type | |
| a. | Hydrilla | ______ |
| b. | Typha | ______ |
| c. | Nymphaea | ______ |
| d. | Lemna | ______ |
| e. | Vallisneria | ______ |
Lianas are vascular plants rooted in the ground and maintain erectness of their stem by making use of other trees for support. They do not maintain direct relation with those trees. Discuss the type of association the lianas have with the trees.
Pick out the appropriate association representing brood parasitism.
Write the observations made at the end of Connell's field, experiment on barnacles on the rocky sea coasts of Scotland.
Match the Column I with Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Lichen | (i) Commensalism |
| B. Shark and Pilot fish | (ii) Mutualism |
| C. Barnacles on the back of a whale | (iii) Symbiotic obligatory relationship |
| D. Sharks and dolphins | (iv) Competition |
The diagram given below shows the life cycle of a malarial parasite. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follows:
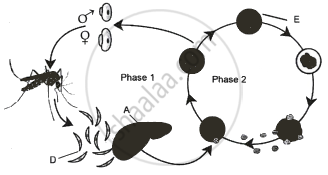
- Name the hosts in which the asexual phase and sexual phase of the life cycle takes place.
- Identify the infective stage labelled ‘D’.
- Name the structure labelled ‘A’ and ‘E’.
- Give any one symptom of malaria.
Some orchids live on the branches of mango trees. Name the type of interaction that exists between the mango tree and the orchid.
Give one example of commensalism.
