Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is the function of radial magnetic field inside the coil?
उत्तर
Moving coil Galvanometer:

Its working is based on the fact that when a current carrying coil is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a torque.
Working:
Suppose the coil PQRS is suspended freely in the magnetic field.
Let, l = Length PQ or RS of the coil
b = Breadth QR or SP of the coil
n = Number of turns in the coil
Area of each turn of the coil, A = l × b
Let B = Strength of the magnetic field in which coil is suspended
I = Current passing through the coil in the direction PQRS
Let, at any instant, α be the angle which the normal drawn on the plane of the coil makes with the direction of magnetic field. The rectangular coil carrying current when placed in the magnetic field experiences a torque whose magnitude is given by,
τ = nIBA sinα
Due to deflecting torque, the coil rotates and suspension wire gets twisted. A restoring torque is set up in the suspension wire.
Let θ be the twist produced in the phosphor bronze strip due to rotation of the coil and K be the restoring torque per unit twist of the phosphor bronze strip. Then,
Total restoring torque produced = kθ
In equilibrium position of the coil,
Deflecting torque = Restoring torque
∴ NIBA = kθ
`or,I = k/(NBA) theta = Gtheta`
Where, `k/(NBA) = G=a` (Constant for a galvanometer)
It is known as galvanometer constant.
• Current sensitivity of the galvanometer is the deflection per unit current. `therefore phi/I = (NAB)/k`
• Voltage sensitivity is the deflection per unit voltage.
`therefore phi/V =(NAB)/k(1/V) = (NAB)/K 1/R (thereforeV= IR)`
The uniform radial magnetic field keeps the plane of the coil always parallel to the direction of the magnetic field. That is, the angle between the plane of the coil and the magnetic field is zero in all the orientations of the coil.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the current flowing through a moving coil galvanometer is directly proportional to the angle of deflection of coil.
Write the underlying principle of a moving coil galvanometer.
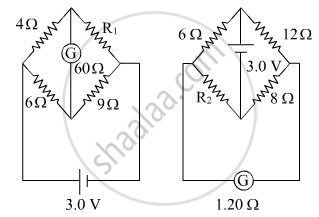
Figure shows two circuits each having a galvanometer and a battery of 3V.
When the galvanometers in each arrangement do not show any deflection, obtain the ratio R1/R2.
Explain, giving reasons, the basic difference in converting a galvanometer into (i) a voltmeter and (ii) an ammeter?
State the principle of the working of a moving coil galvanometer, giving its labeled diagram ?
The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using a ______.
A galvanometer having a coil resistance of 60 Ω shows full-scale deflection when a current of 1.0 amp passes through it. It can be converted into an ammeter to read currents up to 5.0 amp by:
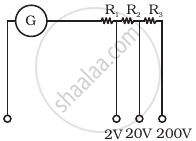
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
How is current sensitivity increased?
