Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw the necessary energy band diagrams to distinguish between conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
How does the change in temperature affect the behaviour of these materials ? Explain briefly.
Write any two distinguishing features between conductors, semiconductors and insulators on the basis of energy band diagrams.
उत्तर १
Conductors: (i) For conductors, the valence band is completely filled and the conduction band can have two possibilities—either it is partially filled with an extremely small energy gap between the valence and conduction bands or it is empty, with the two bands overlapping each other, as shown.

(ii) On applying even an small electric field, conductors can conduct electricity.
Insulators: (i) For insulators, the energy gap between the conduction and valence bands is very large. Also, the conduction band is practically empty, as shown.

(ii) When an electric field is applied across such a solid, the electrons find it difficult to acquire such a large amount of energy to reach the conduction band. Thus, the conduction band continues to be empty. That is why no current flows through insulators.
Semiconductors: (i) The energy band structure of semiconductors is similar to that of insulators, but in their case, the size of forbidden energy gap is much smaller than that of the insulators, as shown.
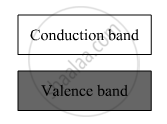
(ii) When an electric field is applied to a semiconductor, the electrons in the valence band find it comparatively easier to shift to the conduction band. So, the conductivity of semiconductors lies between the conductivity of conductors and insulators.
उत्तर २
Energy Band Diagram for a Conductor:
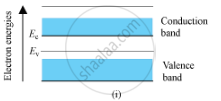
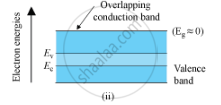
In conductors, the conduction and the valence band overlap each other.
As the temperature increase, the conductivity of the conductors decreases due to increase in the thermal motion of the free electrons.
Energy Band Diagram for an Insulator :

Here, the valence band is completely filled and the conduction band is empty. The energy band gap of the insulator is quite large. So, on increasing the temperature, the electrons of the valence band are not able to reach the conduction band. Therefore, electrical conduction in these materials is impossible.
Energy Band Diagram for a Semiconductor
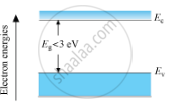
In semiconductors, the valence band is totally filled and the conduction band is empty but the energy gap between conduction band and valence band is quite small. At 0 K, electrons are not able to cross even this small energy gap and, hence, the conduction band remains totally empty. Therefore, the semiconductor at 0 K behaves as an insulator. At room temperature, some electrons in the valence band acquire thermal energy greater than energy band gap, which is less than 3 eV and jump over to the conduction band where they are free to move under the influence of even a small change in the temperature.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How many 1s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions? How many 3s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions?
In a transistor,
In a semiconductor,
(a) there are no free electrons at 0 K
(b) there are no free electrons at any temperature
(c) the number of free electrons increases with temperature
(d) the number of free electrons is less than that in a conductor.
In a pure semiconductor, the number of conduction election 6 × 1019 per cubic metre. How many holes are there in a sample of size 1 cm × 1 mm?
Indium antimonide has a band gap of 0.23 eV between the valence and the conduction band. Find the temperature at which kT equals the band gap.
Estimate the proportion of boron impurity which will increase the conductivity of a pure silicon sample by a factor of 100. Assume that each boron atom creates a hole and the concentration of holes in pure silicon at the same temperature is 7 × 1015 holes per cubic metre. Density of silicon 5 × 1028 atoms per cubic metre.
The product of the hole concentration and the conduction electron concentration turns out to be independent of the amount of any impurity doped. The concentration of conduction electrons in germanium is 6 × 1019 per cubic metref conduction electrons increases to 2 × 1023 per cubic metre. Find the concentration of the holes in the doped germanium.. When some phosphorus impurity is doped into a germanium sample, the concentration o
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
Draw a labelled energy band diagram for a semiconductor.
Three photo diodes D1, D2 and D3 are made of semiconductors having band gaps of 2.5 eV, 2 eV and 3 eV, respectively. Which 0 ones will be able to detect light of wavelength 6000 Å?
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
In which material “Forbidden band” is absent?
