Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how frequency of incident light varies with stopping potential.
उत्तर
1. The effect of frequency of incident light on stopping potential can be studied by keeping the intensity of the incident light constant.
2. The electrode potential varies for different frequencies of the incident light.
3. As the frequency is increased the photoelectrons are emitted with greater kinetic energies so that the retarding potential needed to stop the photoelectrons is also greater.
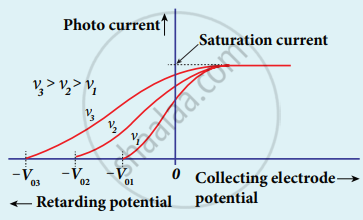
Variation of photocurrent with collector electrode potential for different frequencies of the incident radiation
4. From the graph between frequency and stopping potential, the stopping potential varies linearly with the frequency of the incident light.
5. The stopping potential is zero when no electrons are emitted below a certain frequency called threshold frequency.
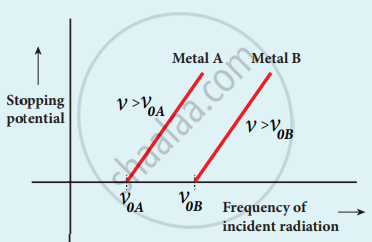
Variation of stopping potential with frequency of the incident radiation for two metals
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the mean wavelength of light from sun is taken as 550 nm and its mean power as 3.8 × 1026 W, then the average number of photons received by the human eye per second from sunlight is of the order of
The threshold wavelength for a metal surface whose photoelectric work function is 3.313 eV is __________.
A light of wavelength 500 nm is incident on a sensitive metal plate of photoelectric work function 1.235 eV. The kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted is (Take h = 6.6 × 10–34 Js)
Define stopping potential.
Explain the quantum concept of light.
Obtain Einstein’s photoelectric equation with the necessary explanation.
List out the characteristics of photons.
Calculate the energies of the photons associated with the following radiation:
- violet light of 413 nm
- X-rays of 0.1 nm
- radio waves of 10 m
When a 6000 Å light falls on the cathode of a photo cell, photoemission takes place. If a potential of 0.8 V is required to stop emission of electron, then determine the
- frequency of the light
- energy of the incident photon
- work function of the cathode material
- threshold frequency and
- net energy of the electron after it leaves the surface.
At the given point of time, the earth receives energy from the sun at 4 cal cm–2 min–1. Determine the number of photons received on the surface of the Earth per cm2 per minute. (Given: Mean wavelength of sunlight = 5500 Å)
