Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how you will determine experimentally the position of the centre of gravity for a triangular lamina (or a triangular piece of cardboard).
उत्तर
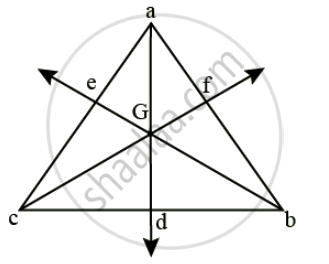
Take a triangular lamina. Make three fine holes at a, b, and c near the edge of the triangular lamina. Now suspend the given lamina along with a plumb line from hole 'a'. Check that the lamina is free to oscillate about the point of suspension. When the lamina has come to rest, draw a straight line ad along the plumb line. Repeat the experiment by suspending the lamina through hole 'b' and then through hole 'c' for which we get straight lines to be and cf, respectively. It is noticed that the lines ad, be and cf intersect each other at a common point G, which is the position of the centre of gravity of the triangular lamina, i.e., the point of intersection of medians.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A uniform half meter rule balances horizontally on a knife-edge at 29 cm mark when a weight of 20 gf is suspended from one end
1) Draw a diagram of the arrangement
2) What is the weight of the half meter rule?
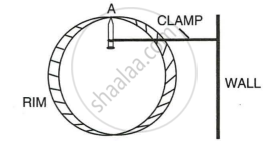
A uniform flat circular rim is balanced on a sharp vertical nail by supporting it at point A, as shown in the figure. Mark the position of the centre of gravity of the rim in the diagram by the letter G.
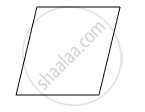
Following Fig shows piece of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into different shapes. Draw two lines to indicate the position of centre of gravity G.

Following Fig shows piece of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into different shapes. Draw two lines to indicate the position of centre of gravity G.
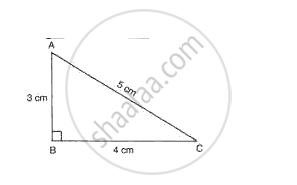
A right-angled triangle cardboard piece is placed as shown in fig. 7. Redraw the diagram showing the relative position of the vertices of the triangle when it is suspended by a pin from the hole A. Explain why the position changes?
Give scientific reason for the following:
There are chances of toppling when a truck takes a sharp turn especially when it is not fully loaded
What is Gravitational force? Give gravitational units of force.
State two methods of increasing the stability of the body.
A boy of mass 40 kg runs up a height of 30 steps, each 20 cm high. Find:
(i) The force of gravity acting on the boy.
(ii) The work done by the boy against gravity. (Take g = 9.8 ms−2)
