Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the bond formation in acetylene.
उत्तर
Similar to ethylene, the bonding in acetylene can also be explained using the hybridization concept. The molecular formula of acetylene is C2H2. The electronic configuration of valence shell of carbon in ground state is [He] 2s2 2px1 2py1 2pz0. To satisfy the valency of carbon promote an electron from 2s orbital to 2pz orbital in the excited state.
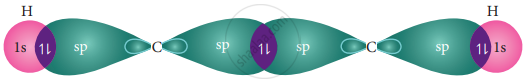
In acetylene molecule, both the carbon atoms are in sp hybridized state. The 2s and 2px orbitals, resulting in two equivalent sp hybridized orbitals lying in a straight line along the molecular axis (x-axis). The unhybridized 2py and 2pz orbitals lie perpendicular to the molecular axis.

Formation of sigma bond:
One of the two sp hybridized orbitals of each carbon linearly overlaps with each other resulting in the formation a C – C sigma bond. The other sp hybridized orbitals of both carbons linearly overlap with the two 1s orbitals of two hydrogen atoms leading to the formation of one C – H sigma bond on each carbon.
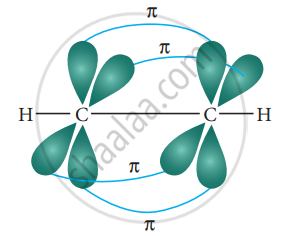
Formation of pi bond:
The unhybridized 2py and 2pz orbitals of each carbon overlap sideways. This lateral overlap results in the formation of two pi bonds (py – py and pz – pz) between the two carbon atoms as shown in the figure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Non – Zero dipole moment is shown by ______.
Define bond order.
Linear form of carbondioxide molecule has two polar bonds. Yet the molecule has Zero dipole moment. Why?
Define bond energy.
Explain resonance with reference to a carbonate ion.
Explain the bond formation in ethylene.
Which one of the following has the highest bond order?
- N2
- N2+
- N2–
Describe Fajan’s rule.
The correct sequence of decrease in the bond angles of the following hydrides is.
The bond order in NO is 2.5 while that in NO+ is 3. Which of the following statements is true for these two species?
