Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the process of electrostatic induction.
दीर्घउत्तर
उत्तर
Whenever a charged rod is touched by another conductor, charges start to flow from charged rod to the conductor. This type of charging without actual contact is called electrostatic induction:
- Consider an uncharged (neutral) conducting sphere at rest on an insulating stand. Suppose a negatively charged rod is brought near the conductor without touching it, as shown in figure (a). The negative charge of the rod repels the electrons in the conductor to the opposite side.
(a)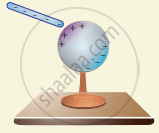
(b)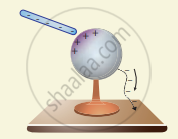
(c)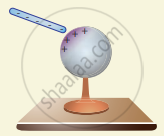
(d)
Various steps in electrostatic induction
As a result, positive charges are induced near the region of the charged rod while negative charges on the farther side. Before introducing the charged rod, the free electrons were distributed uniformly on the surface of the conductor and the net charge is zero. Once the charged rod is brought near the conductor, the distribution is no longer uniform with more electrons located on the farther side of the rod and positive charges are located closer to the rod. But the total charge is zero. - Now the conducting sphere is connected to the ground through a conducting wire. This is called grounding. Since the ground can always receive any amount of electrons, grounding removes the electron from the conducting sphere. Note that positive charges will not flow to the ground because they are attracted by the negative charges of the rod (figure (b)).
- When the grounding wire is removed from the conductor, the positive charges remain near the charged rod (figure (c)).
- Now the charged rod is taken away from the conductor. As soon as the charged rod is removed, the positive charge gets distributed uniformly on the surface of the conductor (figure (d)). By this process, the neutral conducting sphere becomes positively charged.
shaalaa.com
Electrostatics of Conductors and Dielectrics
या प्रश्नात किंवा उत्तरात काही त्रुटी आहे का?
पाठ 1: Electrostatics - Evaluation [पृष्ठ ७४]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write a short note on ‘electrostatic shielding’.
What is polarisation?
What is dielectric strength?
Discuss the various properties of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium.
Explain dielectrics in detail and how an electric field is induced inside a dielectric.
An electron and a proton are allowed to fall through the separation between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor of voltage 5 V and separation distance h = 1 mm as shown in the figure.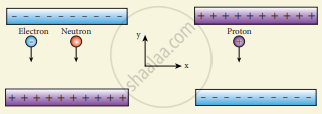
- Calculate the time of flight for both electron and proton.
- Suppose if a neutron is allowed to fall, what is the time of flight?
- Among the three, which one will reach the bottom first?
(Take mp = 1.6 x 10-27 kg, me= 9.1 x 10-31 kg and g = 10 m s-2)
