Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the role of Na+ in the generation of action potential.
उत्तर
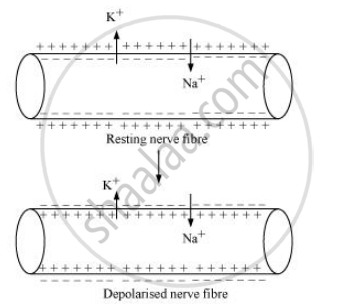
- Sodium ions play an important role in the generation of action potential. When a nerve fibre is stimulated, the membrane potential decreases.
- The membrane becomes more permeable to Na+ ions than to K+ ions. As a result, Na+ diffuses from the outside to the inside of the membrane. This causes the inside of the membrane to become positively charged, while the outer membrane gains a negative charge. This reversal of polarity across the membrane is known as depolarization.
- The rapid inflow of Na+ ions causes the membrane potential to increase, thereby generating an action potential. In the resting state, there is an abundance of negative ions in the axoplasm and positive ions in the tissue fluid.
- There is an accumulation of positive ions on the outer surface of the neurite, or neurilema, and negative ions on the inner surface. There is a positive charge of 70 mV on the outer surface of the nerve cell and a negative charge of 70 mV on the inner surface. In this situation, the nerve sheath, or neurilema, remains in an electrical or depolarized state.
- A lot of potential energy is stored in the neurilema due to the electrical muscle difference around the nerve section. This energy is called resting state potential. Its energy is used in transmission of inspiration.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Compare the following:
Resting potential and action potential
Explain the following process:
Transmission of a nerve impulse across a chemical synapse
Give a brief account of Mechanism of synaptic transmission.
A person is showing symptoms like increased BMR, heart rate, pulse rate, blood pressure and deposition of fats in eye sockets. Name the disease he is suffering from.
Give function of astrocytes in nervous system.
Complete the flowchart of the process of conduction of nerve impulses.
| Application of stimulus on a resting nerve |
| ⇓ |
| Permeability of membrane changes |
| ⇓ |
| ______________________________ |
| ⇓ |
| Positive ions inside axon increases |
| ⇓ |
| ________________________________ |
| ⇓ |
| Polarity reverses and depolarisation takes place |
| ⇓ |
| Repolarisation - potassium gates open |
| ⇓ |
| ______________________________ |
| ⇓ |
| ______________________________ |
| ⇓ |
| Axoplasm becomes negatively charged and ECF becomes positive |
Dendrites transmit impulse ______ cell body and axon transmit impulse ______ cell body.
Which ions is the resting membrane more permeable to?
Match the Column - I with Column - II:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| i. | P - wave | p. | Depolarisation of ventricles |
| ii. | QRS complex | q. | Repolarisation of ventricles |
| iii. | T - wave | r. | Coronary ischemia |
| s. | Development of atria | ||
| t. | Repolarisation of atria |
Neurotransmitters are removed from synaptic cleft by ____________ after transmission of impulse.
Under which of the following conditions will the ionic gradients across the resting membrane be maintained?
Which of the following situations is responsible for resting membrane potential?
Identify the correct path of transmission of nerve impulse.
Potential difference across resting membrane is negative. This is due to differential distribution of the following ions ______.
Resting membrane potential is maintained by ______.
Complete the statement by choosing appropriate match among the following -
| a. Resting potential | i. Chemicals involved in the transmission of impulses at synapses. |
| b. Nerve impulse | ii. Gap between the pre synaptic and post synaptic neurons |
| c. Synaptic cleft | iii. Electrical potential difference across the resting neural membrane |
| d. Neurotransmitters | iv. An electrical wave like response of a neuron to a stimulation |
Write a short note on the following:
Synapse
Write one word for the following:
Point of contact between two nerve cells.
