Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the sexual reproduction process in plants with a diagram.
उत्तर
Sexual reproduction in plants:
- A flower is the functional unit of sexual reproduction in plants.
- The androecium and gynoecium are the male and female parts of the flower respectively.
- The female reproductive organ of a flower which gives rise to egg or female gamete is known as carpel. Ovary present at the base of the carpel contains ovules that undergo meiosis to form embryo sac.
- Stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower which gives rise to male gametes.
- In sexual reproduction of plants, pollination is a major step, which involves the transfer of pollen grains on the stigma of female flower.
- Stigma becomes sticky during pollination.
- The pollen grain germinates over the stigma and gives rise to the pollen tube.
- Pollen tube carries two male gametes which are released near egg cells present in the embryo sac.
- One male gamete fuses with a female gamete giving rise to zygote. The second male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei giving rise to endosperm. This is called as double fertilization.
- Zygote develops into embryo and endosperm serves as a nutritive tissue for the growing embryo.
- After fertilization, the ovule develops into seed and ovary into fruit. Seeds fall upon the ground and can develop into a new plant under favourable conditions.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Mention the changes a flower undergoes after fertilisation.
The anther contains ______.
The process of fusion of the male and female gametes is called ______.
Where are the pollen grains produced?
What are the reproductive organs in a flower?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The ovule becomes a .......... after fertilisation.
Draw a neat sketch of the carpel of a flower. Mark in it stigma, style and ovary.
Give some examples of different modes of fertilisation in nature?
Name the part of a seed which grows into shoot.
What is meant by 'unisexual flowers' and 'bisexual flowers'? Give two examples of each.
When an insect sits on the flower of a plant then some particles A present in the top of little stalks in the flower attach to its body hair. When this insect now sits on the flower of another similar plant, then particles A attached to the hair of insect are put on the top of a flask-shaped organ at the centre of flower. The particle A grows a long tube b from the top of flask-shaped organ through which C moves down and reaches the bottom part of flask-shaped organ. Here C fuses with the nucleus of d contained in structure E. the fusion of C and D forms a new cell f which grows and develops into a seed of the plant.
(a) What are particles A? What is the process of transferring A from one flower to another flower of similar plant by the insect known as?
(b) What is the name of tube B?
(c) What is C which moves down through the tube B?
(d) Name D and E.
(e) What is F?
Fill in the blanks:
A carpel consists of ________ , ________ and ________.
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F):
Flowers which possess stamens and carpel are called unisexual.
Mention the function of Anther.
Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower and label on it sepal, petal, ovary and stigma.
Fill in the blank by selecting suitable word:
Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as______________.
Fill in the blanks and rewrite the completed statements:
Lymph flows in _______________ direction.
Answer the following question.
List two agents of pollination?
Find the odd one out:
Give scientific reason.
Fertilization in plants is called double fertilization.
Distinguish between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Observe the figure below. Write functions of the labelled parts.

The male reproductive part of a flower is ______.
The essential parts of a flower are ______.
Identify the parts A, B, C, and D?
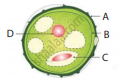
Write the events involved in the sexual reproduction of a flowering plant.
a. Discuss the first event and write the types.
b. Mention the advantages and the disadvantages of that event.
Which of the following is the outermost protective layer of anther?
The 3-celled egg apparatus at the micropylar end comprises of ______
Gloriosa superba exhibits ______.
Sperm and egg nuclei fuse due to ______.
Conidia are formed endogenously while zoospores are formed endogenously.
Give reason for the following:
Fertilization cannot take place in flowers if pollination does not occur.
Trace the path a male gamete takes to fertilise a female gamete after being released from the penis.
State the number of sets of chromosomes present in a zygote.
Double fertilization is essential for formation of ______.
What is puberty?
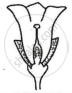
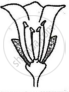
Consider the following three flowers namely X, Y and Z. Which flower(s) would develop into a fruit?
| Flower X | Flower Y | Flower Z |
 |
 |
 |
Explain the post fertilization changes that occur in the ovary of a flower.
