Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the sexual reproduction process in plants with a diagram.
उत्तर
Sexual reproduction in plants:
- A flower is the functional unit of sexual reproduction in plants.
- The androecium and gynoecium are the male and female parts of the flower respectively.
- The female reproductive organ of a flower which gives rise to egg or female gamete is known as carpel. Ovary present at the base of the carpel contains ovules that undergo meiosis to form embryo sac.
- Stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower which gives rise to male gametes.
- In sexual reproduction of plants, pollination is a major step, which involves the transfer of pollen grains on the stigma of female flower.
- Stigma becomes sticky during pollination.
- The pollen grain germinates over the stigma and gives rise to the pollen tube.
- Pollen tube carries two male gametes which are released near egg cells present in the embryo sac.
- One male gamete fuses with a female gamete giving rise to zygote. The second male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei giving rise to endosperm. This is called as double fertilization.
- Zygote develops into embryo and endosperm serves as a nutritive tissue for the growing embryo.
- After fertilization, the ovule develops into seed and ovary into fruit. Seeds fall upon the ground and can develop into a new plant under favourable conditions.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
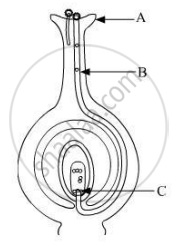
Name the parts A, B and C shown in the diagram and write their functions.
A student while observing an embryo of a pea seed in the laboratory listed various parts of the embryo as given below:
Testa, Tegmen, Radicle, Plumule, Micropyle, Cotyledon.
On examining the list the teacher remarked that only three parts are correct. Select three correct parts from the above list:
(a) Testa, Radicle, Cotyleddon
(b) Tegmen, Radicle, Micropyle
(c) Cotyledon, Plumule, Testa
(d) Radicle, Cotyledon, Plumule
A student identified the various parts of an embryo of a gram seed and listed them as given below :
(I) Testa
(II) Plumule
(III) Radicle
(IV) Cotyledon
(V) Tegmen
Out of these the actual parts of the embryo are :
(A) I, II, III
(B) II, III, IV
(C) III, IV, V
(D) II, IV, V
Write the names of those parts of a flower which serve the same function as the following do in the animals :
(i) testis,
(ii) sperm,
(iii) ovary,
(iv) egg
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Pollen grains contain ............ gametes of a plant.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Ovules contain ......... gametes of a plant.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Flowering plants reproduce by ...........method of reproduction.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The name of the structure in the flower in which the male gamete is formed is...........
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The term used to refer to the transfer of pollen from the stamen of one flower to the carpel of another flower of the same species is...........
Explain the terms 'self pollination'
Name the part of a seed which grows into shoot.
The length of pollen tube depends on the distance between :
(a) pollen grain and upper surface of stigma
(b) pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
(c) pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
(d) upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
What is a flower ? Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the L.S. of a typical flower.
Multiple choice question. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
Unisexual flowers are found in
- mulberry
- mustard
- pea
- sunflower
Fill in the blanks:
A stamen consists of ______ and ________.
Mention the function of Anther.
What are the male and female gametes in a flowering plant?
Draw a labelled diagram of a bisexual flower.
Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram and write their names.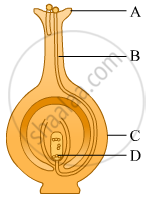
(a) Identify A, B and C in the given diagram and write their functions.
(b) Mention the role of gamete and zygote in sexually reproducing organisms.
In the figure, the parts marked A, B and C are sequentially:

(A) Plumule, Radicle and Cotyledon
(B) Radicle, Plumule and Cotyledon
(C) Plumule, Cotyledon and Radicle
(D) Radicle, Cotyledon and Plumule
Draw a diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth into the ovule and label the following:
Pollen grain, male gamete, female gamete, ovary.
Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower and label on it sepal, petal, ovary and stigma.
What is cleistogamy? Write one advantage and one disadvantage of it, to the plant.
Answer the following question.
List two agents of pollination?
Pollen grains are formed by _________ division in locules of anthers.
Find an odd one out.
In which part of the flower germination of pollen grains takes place?
How many middle layers are generally present in the wall of the anther lobes?
The 3-celled egg apparatus at the micropylar end comprises of ______
The flower of the Hibiscus plant is ______
Pollen grains are produced by ______
Complete the table
| Carly x | ______ | ______ |
| ______ | petal | attract insects |
| Androecium | ______ | Male reproductive part |
| ______ | ______ | Female reproductive part. |
Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
- They possess both stamen and pistil
- They possess either stamen or pistil
- They exhibit cross pollination
- Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
In a bisexual flower inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Provide a suitable explanation for the above situation.
Is the chromosome number of zygote, embryonal cells and adult of a particular organism always constant? How is the constancy maintained in these three stages?
State the number of sets of chromosomes present in a zygote.
Name the reproductive parts of an angiosperm. Where are these parts located? Explain the structure of its male reproductive part.
- Assertion: Primary endosperm nucleus is diploid.
- Reason: It is the product of double fertilisation.
