Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 1
▶ 3: Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2
4: Environmental Management
5: Towards Green Energy
6: Animal Classification
7: Introduction to Microbiology
8: Cell Biology and Biotechnology
9: Social Health
10: Disaster Management
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 3 - Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 3 - Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-and-technology-2-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of Maharashtra State Board SCERT Maharashtra for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Choose the correct option
Choose the correct option.
In humans, there are ____________ pairs of chromosomes.
22
23
44
46
Which of the following is not a type of asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms?
Fragmentation
Regeneration
Budding
Binary fission
Find the odd one out:
Stigma
Anther
Style
Ovary
At the time of birth, there are _______________ oocytes in the ovary of a female foetus.
1 to 2 million
2 to 3 million
2 to 4 million
none of these
____________ modern remedial technique is used if there is a problem in implantation of embryo in the uterus.
Surrogacy
Sperm bank
In vitro fertilization
none of these
Implantation of the embryo occurs in ________.
uterus
ovary
oviduct
vagina
In humans, sperm production occurs in the organ ______.
testes
scrotum
prostate gland
ovaries
vas deferens
ejaculatory duct
urinogenital duct
Pregnant mother supplies nourishment to her foetus through ___________.
uterus
placenta
ovary
oviduct
___________ twins are formed from a single embryo.
Dizygotic
Monozygotic
Multiple zygotes
Zygote
Pollen grains are formed by _________ division in locules of anthers.
meiosis
mitosis
amitosis
binary
Asexual reproduction occurs by __________ cell division.
mitotic
meiotic
fertilization
double fertilization
This method of asexual reproduction is seen in paramoecium.
transverse binary fission
longitudinal binary fission
simple binary fission.
regeneration
In meiosis, the number of chromosomes becomes ___________.
multiple times
triple
half
double
Generally, every month, __________ ovum is released in the abdominal cavity alternately from each ovary.
1
2
3
4
__________ is present in unisexual flower.
Both androecium and gynoecium
Only androecium
Only gynoecium
Androecium or gynoecium
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Find an odd one out
Find an odd one out.
Budding
Regeneration
Binary fission
Fragmentation
Find an odd one out.
Vas efferens
Prostate gland
Epididymis
Vas deferens
Find an odd one out.
Prostate glands
Bartholin glands
Cowper’s gland
Seminal vesicle
Find an odd one out.
Stigma
Style
Pollens
Ovary
Find an odd one out.
Hibiscus
Papaya
Sun-flower
Rose
Mango
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Name the following
Name the following.
Hormones related to male reproductive system.
Modern technologies in reproduction.
Hormones secreted by the ovary of the female reproductive system.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Relate the following
Relate the following.
Amoeba : fission : : Hydra : ____________
Calyx : Sepals : : Corolla : ________________
Bisexual : Hibiscus : : Unisexual : ___________
Follicle stimulating hormone : Development of oocyte : : Luteinizing hormone : ____________
Accessory whorls : Calyx and corolla : : essential whorls : ______________
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Write true or false
Write whether true or false.
Pollen tube reaches the embryo sac via style.
True
False
Sometimes twins are genetically different.
True
False
Pollen grains from anther are transferred to the stigma.
True
False
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Define
Define.
Fragmentation
Define.
Vegetative propagation
Define.
Fertilization
Define.
Regeneration
Define.
Inflorescence
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Answer in one sentence
Answer in one sentence.
What is gamete formation?
Name the two types of twins.
Write any two Sexually transmitted diseases.
What determines whether the two organisms of a species will be exactly similar or not?
How are the sperms formed?
How is the semen produced?
Which are the components of pollination?
Which parts are converted into Seed and fruit respectively after fertilization?
What does germination mean?
Write the name of the type of reproduction in the following figure.

How can plants and animals save themselves from extinction?
Name the three types of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms.
Write the functions of ovary
Write the functions of sepals
Write the functions of penis
Write the functions of Seminal vesicle
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Give scientific reasons
Give scientific reason.
Flower is a structural unit of sexual reproduction in plants.
Give scientific reason.
Older women are more likely to give birth to children with some abnormalities.
Give scientific reason.
Fertilization in plants is called double fertilization.
Give scientific reason.
There is a menopause when women are 45-50 years old.
Give scientific reason.
The new individual produced by sexual reproduction always has the recombined genes of both the parents.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Solve the following questions
Solve the following subquestions.
Identify the type of reproduction from the following explanation and draw a neat and labelled diagram.
- The body of the parent organism breaks up into many fragments and each fragment starts to live as an independent new organism.
- Give two examples of living organisms which follow this type of reproduction method.
Distinguish between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Distinguish between sexual and asexual reproduction.
Explain the process of fertilization.
State names of organs in male reproductive system.
State names of organs in the female reproductive system.
Explain asexual reproduction in plants.
What would be the effect if meiosis did not occur in nature?
What is reproduction?
Explain the importance of the reproduction process.
Explain two main process in sexual reproduction.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Write short notes
Write a short note.
Budding in Hydra
Explain the following concept in short:
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Write a short note.
Reasons of infertility
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Distinguish between
Distinguish between the following.
Binary fission and Multiple fission
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Answer the following questions
Answer the following questions.
A married couple does not have children even after the necessary tests, so what are the solutions you would suggest?
Why is it necessary to maintain reproductive health? Which precautions one should follow to maintain reproductive health?
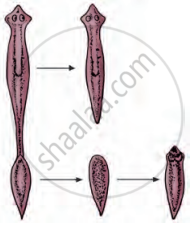
Observe the given diagram and explain the method of reproduction.
A piece of wet bread or bhakri kept in a humid place for 2-3 days, then
- What will you observe?
- State the scientific name of the living organism and write its characteristics.
Observe the given picture and answer the questions given below.

- State the type of reproduction.
- Identify the part of reproduction.
Sweet potato - _____________
Bryophyllum - _____________
Potato - _____________
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

- Label the indicated parts 1, 2 and 3 in the diagram.
- Where the fertilization of ovum occurs?
- Where does the embryo get implanted after fertilization?
- Which type of reproduction is indicated in the following diagram?
- Redraw the given type of reproduction in the correct sequence and explain it.

Complete the paragraph with the help of words given in the bracket.
(Luteinizing hormone, endometrium of uterus, follicle stimulating hormone, estrogen, progesterone, corpus luteum)
Growth of follicles present in the ovary occurs under the effect of ____________. This follicle secretes estrogen. _____________ grows/regenerates under the effect of estrogen. Under the effect of ___________, fully grown up follicle bursts, ovulation occurs and _______________ is formed from remaining part of follicle. It secrets ____________ and __________. Under the effect of these hormones, glands of ____________ are activated and it becomes ready for implantation.
What is the menstrual cycle?
State the names of four hormones which control menstrual cycle.
If newborns are produced at the age of menopause, they may be with some abnormalities. Why?
Complete the table.
| Sex/Gender | Reasons of infertility |
| Female | |
| Male |
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Solve the following questions
Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Double fertilization in angiosperms
Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Human male reproductive organs
Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Spore formation
Sketch the labeled diagram:
Human female reproductive system
Write the answers to the following questions by observing the figure below.

- What does the figure above show?
- Which organs are involved in this process?
- Which hormones are involved in this process?
- After how many days do these changes happen again?
- Explain your opinion about the statement that a woman's body is impure while the above process is going on.
Explain the sexual reproduction process in plants with a diagram.
Observe the figure below. Write functions of the labelled parts.

Read the following paragraph and write the answers to the questions based on it.
Reproduction is an important process for the survival of an organism. Asexual reproduction occurs in different ways in plants. E.g. Vegetative propagation, fragmentation, budding, spore formation etc. Gametes are formed for sexual reproduction. In the animal kingdom, various methods like budding, binary fission, and parthenogenesis are used. There is no difference between males and females in the animals in which these methods are observed. The method of regeneration also creates new organisms. But regeneration is not the real method of reproduction. Regeneration is the process of healing wounds, creating new organs. This ability has completely disappeared in the developed animals. Modern research is being done on the method of sexual reproduction, e.g. Cloning. So, in the future women will be able to create their own offspring without a father.
- How do living organisms maintain their own species continuity?
- What are the methods of asexual reproduction in animals?
- Why is it said that regeneration is not the real method of reproduction?
- What are the different methods of reproduction in plants?
- What modern breeding methods are being researched in developed animals?
‘Surrogacy, In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), Sperm Bank/Semen Bank etc. modern technology will be useful to humans.’ support this statement.
Write the answers to the questions by observing the figure.

- What does the above figure show?
- Write the names of parts A, B, C, D.
- Write the function of the part 'D'.
- How is semen formed?
- What process does the next figure show?
- Describe in short that process.
- Who can benefit from this process?
Solutions for 3: Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 3 - Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 3 - Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-and-technology-2-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 3 - Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 3 (Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. SCERT Maharashtra textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 3 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 are Parturition (Birth) in Human, Asexual Reproduction in Animal, Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle), Human Reproduction, Fertilization in Human, Asexual Reproduction in Plant, Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants, Reproduction, Sexual Reproduction in Animals, The Male Reproductive System, The Female Reproductive System, Gametogenesis, Embryonic Development in Human, Implantation in Human, Pregnancy in Humans, Placenta (Growth) in Human, Budding, Vegetative Reproduction, Reproduction and Modern Technology, Reproductive Health, Introduction to Life Processes in Living Organisms, Fission, Fragmentation, Regeneration, Budding, Sporulation (Sporogenesis).
Using SCERT Maharashtra Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC solutions Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in SCERT Maharashtra Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC students prefer SCERT Maharashtra Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC additional questions for Mathematics Science and Technology 2 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
